| 1 |
Recurrent recessive mutation in deoxyguanosine kinase causes idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension.Hepatology. 2016 Jun;63(6):1977-86. doi: 10.1002/hep.28499. Epub 2016 Mar 31.
|
| 2 |
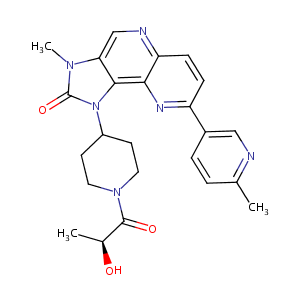
Discovery of the Highly Potent PI3K/mTOR Dual Inhibitor PF-04979064 through Structure-Based Drug Design. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2012 Nov 7;4(1):91-7.
|
| 3 |
ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00666926) Study Of PF-00562271, Including Patients With Pancreatic, Head And Neck, Prostatic Neoplasms. U.S. National Institutes of Health.
|
| 4 |
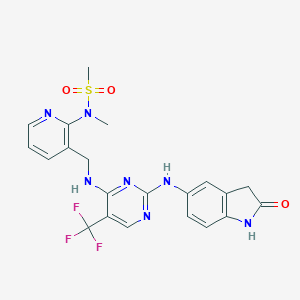
Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase by PF-562,271 inhibits the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer concomitant with altering the tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Nov;10(11):2135-45.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|