Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMFETDK)
| Drug Name |
Artemisinin SP
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Isoguvacine; isoguvacine; 1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-4-carboxylic acid; 64603-90-3; 1,2,3,6-Tetrahydro-pyridine-4-carboxylic acid; 1,2,3,6-Tetrahydro-4-pyridinecarboxylic acid; UNII-YTF580771Y; CHEMBL39071; CHEBI:34799; YTF580771Y; 4-Pyridinecarboxylic acid, 1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-; AC1OEMUS; 1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridinium-4-carboxylate; 1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylate; Tocris-0235; Spectrum_001974; Lopac-G-002; AC1L1GNT; Spectrum3_001869; Biomol-NT_000254; AC1Q5QG1; Lopac0_000561; KBioSS_002540; BSPBio_003318; DivK1c_000115
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
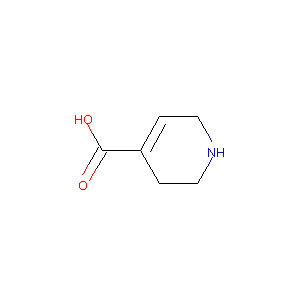 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 1 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 127.14 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -2.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Malaria | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | 1F40-1F45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
