Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMKS1DV)
| Drug Name |
SARALASIN
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Saralasin; 34273-10-4; UNII-H2AFV2HE66; (Sar1,Val5,Ala8)-Angiotensin II; CHEMBL938; H2AFV2HE66; Saralasinum [INN-Latin]; Saralasin [INN:BAN]; Saralasine [INN-French]; Saralasina [INN-Spanish]; Saralasinum; Saralasine; Saralasina; (1-(N-Methylglycin) 5-L-valin, 8-L-alanin)angiotensin II; Angiotensin II, 1-(N-methylglycine)-5-L-valine-8-L-alanine-; NCGC00166135-01; N-(1-(N-(N-(N-(N-(N2-(N-methylglycly)-L-arginyl)-L-valyl)-L-tyrosyl)-L-valyl)-L-histidyl)-L-prolyl)-L-alanine; SCHEMBL23; AC1O44IX; DSSTox_RID_81710
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
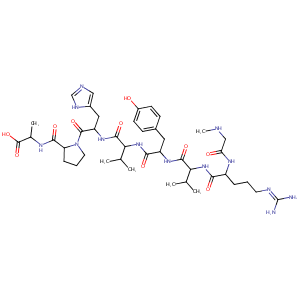 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 5 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 912 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -2.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Hypertension | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | BA00-BA04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
