| 1 |
Recurrent recessive mutation in deoxyguanosine kinase causes idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension.Hepatology. 2016 Jun;63(6):1977-86. doi: 10.1002/hep.28499. Epub 2016 Mar 31.
|
| 2 |
URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 80).
|
| 3 |
Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77.
|
| 4 |
Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA)
|
| 5 |
Pharmacological characterization of recombinant human 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptors using a novel antagonist radioligand, [3H]WAY-100635. Life Sci. 1997;60(9):653-65.
|
| 6 |
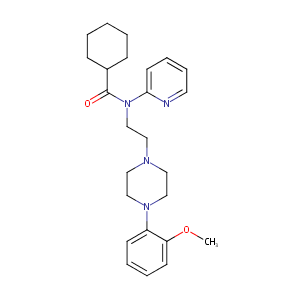
Design, synthesis, radiolabeling, and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of bridgehead iodinated analogues of N-{2-[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl}-N-(pyridin-2-yl)cyclohexanecarboxamide (WAY-100635) as potential SPECT ligands for the 5-HT1A receptor. J Med Chem. 2011 May 26;54(10):3480-91. doi: 10.1021/jm1009956. Epub 2011 Apr 26.
|
| 7 |
2006 drug approvals: finding the niche. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007 Feb;6(2):99-101.
|
| 8 |
Impact of drug transporters on cellular resistance towards saquinavir and darunavir. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010 Nov;65(11):2319-28.
|
| 9 |
Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1: a genetically polymorphic transporter of major importance for hepatic drug uptake. Pharmacol Rev. 2011 Mar;63(1):157-81.
|
| 10 |
P-glycoprotein mediates efflux transport of darunavir in human intestinal Caco-2 and ABCB1 gene-transfected renal LLC-PK1 cell lines. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009 Sep;32(9):1588-93.
|
| 11 |
Drug interactions with new and investigational antiretrovirals. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009;48(4):211-41.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|