| 1 |
Recurrent recessive mutation in deoxyguanosine kinase causes idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension.Hepatology. 2016 Jun;63(6):1977-86. doi: 10.1002/hep.28499. Epub 2016 Mar 31.
|
| 2 |
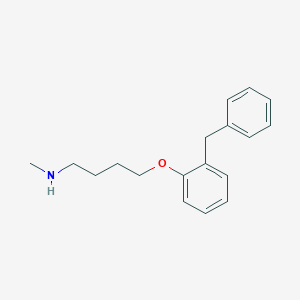
4-(O-benzylphenoxy)-N-methylbutylamine (bifemelane) and other 4-(O-benzylphenoxy)-N-methylalkylamines as new inhibitors of type A and B monoamine oxidase. J Neurochem. 1988 Jan;50(1):243-7.
|
| 3 |
The fight against drug-resistant malaria: novel plasmodial targets and antimalarial drugs. Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(2):161-71.
|
| 4 |
Why are most phospholipidosis inducers also hERG blockers?. Arch Toxicol. 2017 Dec;91(12):3885-3895. doi: 10.1007/s00204-017-1995-9. Epub 2017 May 27.
|
| 5 |
Inhibitor binding in a class 2 dihydroorotate dehydrogenase causes variations in the membrane-associated N-terminal domain. Protein Sci. 2004 Apr;13(4):1031-42.
|
| 6 |
Time-dependent pharmacokinetics and drug metabolism of atovaquone plus proguanil (Malarone) when taken as chemoprophylaxis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2002 Apr;58(1):19-27.
|
| 7 |
Kinetics of inhibition of human and rat dihydroorotate dehydrogenase by atovaquone, lawsone derivatives, brequinar sodium and polyporic acid. Chem Biol Interact. 2000 Jan 3;124(1):61-76.
|
| 8 |
Application of higher throughput screening (HTS) inhibition assays to evaluate the interaction of antiparasitic drugs with cytochrome P450s. Drug Metab Dispos. 2001 Jan;29(1):30-5.
|
| 9 |
Loss of function mutations in VARS encoding cytoplasmic valyl-tRNA synthetase cause microcephaly, seizures, and progressive cerebral atrophy.Hum Genet. 2018 Apr;137(4):293-303. doi: 10.1007/s00439-018-1882-3. Epub 2018 Apr 24.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|