| Drug Name |
Arotinolol
|
| Synonyms |
Arotinolol; Arotinolol (INN); Arotinolol [INN]; Arotinololum; Arotinololum [Latin]; (+-)-5-(2-((3-(tert-Butylamino)-2-hydroxypropyl)thio)-4-thiazolyl)-2-thiophenecarboxamide; 2-(3-tert-Butylamino-2-hydroxypropylthio)-4-(5-carbamoyl-2-thienyl)thiazole; 5-(2-((3-(tert-Butylamino)-2-hydroxypropyl)thio)thiazol-4-yl)thiophene-2-carboxamide; 5-[2-[3-(tert-butylamino)-2-hydroxypropyl]sulfanyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]thiophene-2-carboxamide; 68377-92-4; AK129719; C15H21N3O2S3; S-596
|
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
| Structure |
|
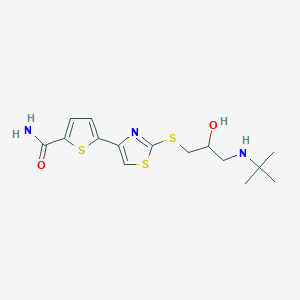 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 |
Molecular Weight (mw) |
371.5 |
|
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) |
2.3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) |
8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) |
3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) |
7 |
| ADMET Property |
- Absorption Tmax
-
The time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) is 2 h
[1]
- Half-life
-
The concentration or amount of drug in body reduced by one-half in 7.2 hours
[2]
|
| Chemical Identifiers |
- Formula
- C15H21N3O2S3
- IUPAC Name
5-[2-[3-(tert-butylamino)-2-hydroxypropyl]sulfanyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]thiophene-2-carboxamide - Canonical SMILES
-
CC(C)(C)NCC(CSC1=NC(=CS1)C2=CC=C(S2)C(=O)N)O
- InChI
-
BHIAIPWSVYSKJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- InChIKey
-
1S/C15H21N3O2S3/c1-15(2,3)17-6-9(19)7-21-14-18-10(8-22-14)11-4-5-12(23-11)13(16)20/h4-5,8-9,17,19H,6-7H2,1-3H3,(H2,16,20)
|
| Cross-matching ID |
- PubChem CID
- 2239
- ChEBI ID
-
- CAS Number
-
- UNII
-
- DrugBank ID
-
- INTEDE ID
- DR0138
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

