Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMV2DIW)
| Drug Name |
BAY 10-00394
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | roniciclib; BAY 1000394; BAY 10-00394; KB-145902; 1223498-69-8; Tube010; SCHEMBL875845; GTPL7874 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
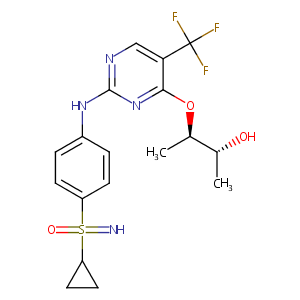 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 430.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 4.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Small-cell lung cancer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | 2C25.Y | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
