Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMV7IM6)
| Drug Name |
Histamine Phosphate
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Histamine acid phosphate; Histamine biphosphate; Histamine dihydrogen phosphate; Histamine diphosphate; Histamine phosphate [USP]; Histamine positive; H0147; Histamine phosphate (TN); Histamine phosphate (USP); Histamine phosphate (1:2); 1H-Imidazole-4-ethanamine, phosphate (1:2); 2-Imidazol-4-ylethylamine orthophosphoric acid (1:2); 4-(2-Aminoethyl)imidazole bis(dihydrogen phosphate); 4-(2-Aminoethyl)imidazole di-acid phosphate; 4-2(2-Aminoethyl)Imidazole-Di-Acid Phosphate
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Diagnostic Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
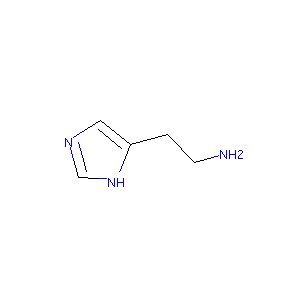 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 1 |
Molecular Weight | 307.14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
