Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMZI2UF)
| Drug Name |
Sulphadoxine
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2447-57-6; Sulforthomidine; Fanasil; Sulphormethoxine; 4-amino-N-(5,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide; Sulfadoxinum; Sulfadoxina; Sulfadoxin; Fanzil; Solfadossina; Ro 4-4393; Solfadossina [DCIT]; Sulfadoxinum [INN-Latin]; Sulfadoxina [INN-Spanish]; 4-Sulfanilamido-5,6-dimethoxypyrimidine; 4-Amino-N-(5,6-dimethoxy-4-pyrimidinyl)benzenesulfonamide; Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-(5,6-dimethoxy-4-pyrimidinyl)-; WR 4873; N'-(5,6-Dimethoxy-4-pyrimidyl)sulfanilamide; UNII-88463U4SM5; Orthosulfin; Sulformethoxine; Sulformetoxine; Sulphormetoxin; Sulphorthodimethoxine; WR 4073; Ro-4-4393; Sanasil: Sulfadoxine: Sulformetoxin; Sulfadoxine (JAN/USP/INN); Sulfadoxine [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN]; N1-(5,6-Dimethoxy-4-pyrimidinyl)sulfanilamide; N(sup 1)-(5,6-Dimethoxy-4-pyrimidinyl)sulfanilamide; 4-amino-N-[5,6-bis(methyloxy)pyrimidin-4-yl]benzenesulfonamide; 6-(4-Aminobenzenesulfonamido)-4,5-dimethoxypyrimidine; RS-1653
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
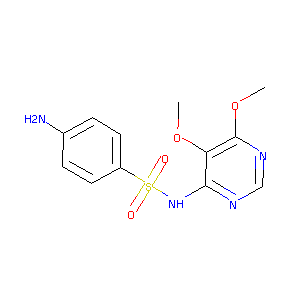 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 310.33 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 0.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Malaria | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | 1F40-1F45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Sulphadoxine (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
