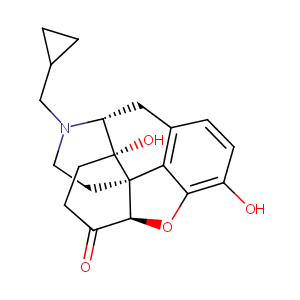
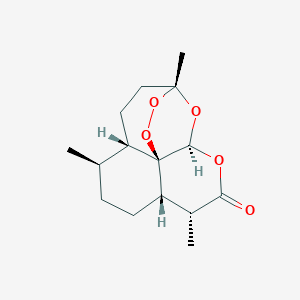
| 1 |
Recurrent recessive mutation in deoxyguanosine kinase causes idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension.Hepatology. 2016 Jun;63(6):1977-86. doi: 10.1002/hep.28499. Epub 2016 Mar 31.
|
| 2 |
Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015
|
| 3 |
FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2019. Application Number: (ANDA) 074918.
|
| 4 |
Naltrexone FDA Label
|
| 5 |
URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 1639).
|
| 6 |
ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04365985) Study of Immunomodulation Using Naltrexone and Ketamine for COVID-19. U.S. National Institutes of Health.
|
| 7 |
The fight against drug-resistant malaria: novel plasmodial targets and antimalarial drugs. Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(2):161-71.
|
| 8 |
An evaluation of mu-opioid receptor (OPRM1) as a predictor of naltrexone response in the treatment of alcohol dependence: results from the Combined Pharmacotherapies and Behavioral Interventions for Alcohol Dependence (COMBINE) study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2008 Feb;65(2):135-44.
|
| 9 |
In vivo chronic exposure to heroin or naltrexone selectively inhibits liver microsome formation of estradiol-3-glucuronide in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008 Sep 1;76(5):672-9.
|
| 10 |
Low dose naltrexone therapy in multiple sclerosis. Med Hypotheses. 2005;64(4):721-4.
|
| 11 |
Chronic naltrexone treatment induces desensitization of the luteinizing hormone pulse generator for opioid blockade in hyperprolactinemic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995 May;80(5):1739-42. doi: 10.1210/jcem.80.5.7745028.
|
| 12 |
Association between the Stin2 VNTR polymorphism of the serotonin transporter gene and treatment outcome in alcohol-dependent patients. Alcohol Alcohol. 2008 Sep-Oct;43(5):516-22. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agn048. Epub 2008 Jun 14.
|
| 13 |
Predicting the effect of naltrexone and acamprosate in alcohol-dependent patients using genetic indicators. Addict Biol. 2009 Jul;14(3):328-37.
|
| 14 |
Antimalarial artemisinin drugs induce cytochrome P450 and MDR1 expression by activation of xenosensors pregnane X receptor and constitutive androstane receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 2005 Jun;67(6):1954-65.
|
| 15 |
Identification of the human cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in the in vitro metabolism of artemisinin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1999 Oct;48(4):528-35.
|
| 16 |
Inhibition of glutathione S-transferases by antimalarial drugs possible implications for circumventing anticancer drug resistance. Int J Cancer. 2002 Feb 10;97(5):700-5.
|
| 17 |
Antimalarial artemisinin drugs induce cytochrome P450 and MDR1 expression by activation of xenosensors pregnane X receptor and constitutive androstane receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 2005 Jun;67(6):1954-65.
|
| 18 |
Application of higher throughput screening (HTS) inhibition assays to evaluate the interaction of antiparasitic drugs with cytochrome P450s. Drug Metab Dispos. 2001 Jan;29(1):30-5.
|
| 19 |
Identification of Compounds That Inhibit Estrogen-Related Receptor Alpha Signaling Using High-Throughput Screening Assays. Molecules. 2019 Feb 27;24(5):841. doi: 10.3390/molecules24050841.
|
| 20 |
In vivo and mechanistic evidence of nuclear receptor CAR induction by artemisinin. Eur J Clin Invest. 2006 Sep;36(9):647-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2006.01700.x.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|