Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM1HMWA)
| Drug Name |
2'-Deoxyuridine
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2'-DEOXYURIDINE; 951-78-0; deoxyuridine; Uracil deoxyriboside; 1-((2R,4S,5R)-4-Hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione; 2-Deoxyuridine; Deoxyribose uracil; 2'-Desoxyuridine; UNII-W78I7AY22C; CCRIS 2832; dURD; EINECS 213-455-7; BRN 0024433; 1-(2-Deoxy-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)uracil; W78I7AY22C; CHEBI:16450; 2 -Deoxyuridine; 1-(2-Deoxy-beta-D-erythro-pentofuranoxyl)uracil; MFCD00006527; AK-54658; 2,4(1H,3H)-Pyrimidinedione, 1-(2-deoxy-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-; NSC 23615; DEOXYURIDINE
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
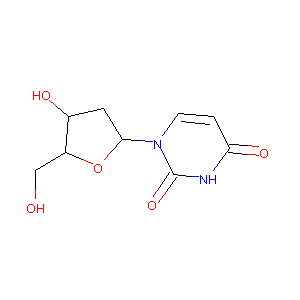 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 228.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -1.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Discovery agent | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | N.A. | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
