Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMEZO4M)
| Drug Name |
G6976
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
12H-Indolo[2,3-a]pyrrolo[3,4-c]carbazole-12-propanenitrile, 5,6,7,13-tetrahydro-13-methyl-5-oxo-; Go 6976; 136194-77-9; GO6976; Go-6976; Goe 6976; UNII-B9IQO7JZ16; 6976; Go 6976, Solution; B9IQO7JZ16; 5,6,7,13-Tetrahydro-13-Methyl-5-oxo-12H-indolo[2,3-a]pyrrolo[3,4-c]carbazole-12-propanenitrile; CHEMBL302449; CHEBI:51913; 12-(2-Cyanoethyl)-6,7,12,13-tetrahydro-13-methyl-5-oxo-5H-indolo[2,3-a]pyrrolo[3,4-c]carbazole; 12-(2-Cyanoethyl)-6,7,12,13-tetrahydro-13-methyl-5-oxo-5H-indolo(2,3-a)pyrrolo(3,4-c)-carbazole; Go6976
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
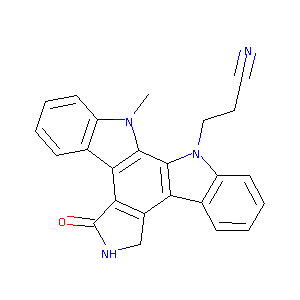 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 378.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 3.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
