Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMGQF3R)
| Drug Name |
Remoxipride
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Remoxiprida; Remoxipridum; Romoxipride; A 33547; FLA 731; A-33547; FLA-731; Remoxiprida [INN-Spanish]; Remoxipride (USAN); Remoxipridum [INN-Latin]; Remoxipride [USAN:BAN:INN]; (-)-(S)-3-Brom-N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-2,6-dimethoxybenzamid; (-)-(S)-3-Bromo-N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-2,6-dimethoxybenzamide; (-)-n-ethyl-2-(3-bromo-2,6-dimethoxybenzamidomethyl)pyrrolidine; (S)-3-Bromo-2,6-dimethoxy-N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)benzamide; (S)-3-Bromo-N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-2,6-dimethoxybenzamide; 3-bromo-N-[[(2S)-1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl]methyl]-2,6-dimethoxybenzamide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antipsychotic Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
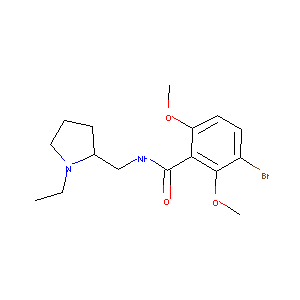 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 371.27 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 2.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Schizophrenia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | 6A20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
