Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMUB0EC)
| Drug Name |
VELNACRINE
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Velnacrine; 124027-47-0; 1-hydroxytacrine; 9-amino-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridin-1-ol; Velnacrine [INN:BAN]; Velnacrinum [INN-Latin]; Velnacrina [INN-Spanish]; 1-Acridinol,9-amino-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-; 104675-29-8; 1-Acridinol, 9-amino-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-; UNII-JFN3Z63E2C; UNII-OQL6V4U301; JFN3Z63E2C; CHEMBL51934; OQL6V4U301; HLVVITIHAZBPKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N; AK160411; Velnacrinum; Velnacrina; 112964-98-4; Velnacrine, (+)-; 9-ATHCO; 1-hydroxy-tacrine; 1-Hydroxy Tacrine; 121445-17-8; ACMC-20ddjc; Velnacrine, (-)-; Spectrum_000073; AC1Q7AWG
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
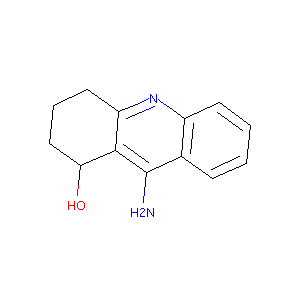 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 214.26 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 1.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Cognitive impairment | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | 6D71 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
