Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM28CLZ)
| Drug Name |
2-Phenyl-1,2-dihydro-indazol-3-one
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
3-Indazolinone, 2-phenyl-; 2-phenyl-1H-indazol-3-one; 17049-65-9; MLS-0315919.0001; CHEMBL412902; 2-phenylindazolone; NSC34813; 2-Phenyl-1,2-dihydro-indazol-3-one; 2-phenylindazolin-3-one; 3H-Indazol-3-one, 1,2-dihydro-2-phenyl-; AC1L91HU; cid_411519; SCHEMBL2438599; CHEMBL1719803; BDBM46671; DTXSID20328536; CFNJFZDGHGYAMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N; NSC-34813; ZINC84460115; AKOS023543908; 3H-Indazol-3-one,2-dihydro-2-phenyl-; 1,2-Dihydro-2-phenyl-3H-indazol-3-one; 2-Phenyl-1,2-dihydro-3H-indazol-3-one #
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
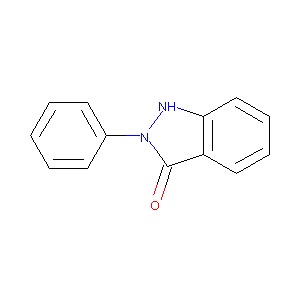 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 210.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 2.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Discovery agent | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | N.A. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
