Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMH5W0G)
| Drug Name |
Dipivefrin
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
AKPro; Dipivefrina; Dipivefrine; Dipivefrinum; Propine; Dipivalyl epinephrine; Dipivefrin HCL; Dipivefrin [USAN]; K 30081; Dipivefrin (USAN); Dipivefrina [INN-Spanish]; Dipivefrine (INN); Dipivefrinum [INN-Latin]; Ophtho-Dipivefrin; Propine C Cap B.I.D.; [2-(2,2-dimethylpropanoyloxy)-4-[1-hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl]phenyl] 2,2-dimethylpropanoate; (+-)-3,4-Dihydroxy-alpha-((methylamino)methyl)benzyl alcohol 3,4-dipivalate; (+-)-4-[1-hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl]-o-phenylene divavalate; (-)-2,2-Dimethylpropansaeure-4-(1-hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl)-1,2-phenylenester; (-)-4-(1-Hydroxy-2-methylaminoethyl)-o-phenylendipivalat; (RS)-4-(1-Hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl)-1,2-phenylen dipivalat; 1-(3',4'-dipivaloyloxyphenyl)-2-methylamino-1-ethanol; 2,2-Dimethylpropanoic acid 4-[1-hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl]-1,2-phenylene ester; 4-(1-Hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl)-1,2-phenylen dipivalat; 4-[1-hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl]-o-phenylene divavalate; 4-[1-hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl]benzene-1,2-diyl bis(2,2-dimethylpropanoate)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Ophthalmologicals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
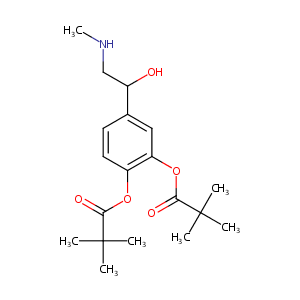 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 351.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 2.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Dipivefrin (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Contractile response of the isolated trabecular meshwork and ciliary muscle to cholinergic and adrenergic agents. Ger J Ophthalmol. 1996 May;5(3):146-53. | ||||
| 3 | Cusson JR, Goldenberg E, Larochelle P "Effect of a novel monoamine-oxidase inhibitor, moclobemide on the sensitivity to intravenous tyramine and norepinephrine in humans." J Clin Pharmacol 31 (1991): 462-7. [PMID: 2050833] | ||||
| 4 | Product Information. Cymbalta (duloxetine). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 5 | Barthel W, Glusa E, Koth W "Interactions of dihydroergotamine with etilefrine in human leg veins in vitro and in situ." Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 25 (1987): 63-9. [PMID: 2881898] | ||||
| 6 | Mendelson J, Jones RT, Upton R, Jacob P 3rd "Methamphetamine and ethanol interactions in humans." Clin Pharmacol Ther 57 (1995): 559-68. [PMID: 7768079] | ||||
