Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMH7IDQ)
| Drug Name |
Dichlorphenamide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
dichlorphenamide; Diclofenamide; 120-97-8; 4,5-dichlorobenzene-1,3-disulfonamide; Dichlofenamide; Dichlorophenamide; Daranide; Dichlorphenamid; Glauconide; Antidrasi; Glaucol; Oratrol; Diclofenamidum; Diclofenamida; Diclofenamid; Barastonin; Glaumid; Glafco; Glajust; 4,5-Dichloro-m-benzenedisulfonamide; 1,3-Benzenedisulfonamide, 4,5-dichloro-; Diclofenamidum [INN-Latin]; 4,5-Dichloro-1,3-disulfamoylbenzene; 1,3-Disulfamoyl-4,5-dichlorobenzene; Diclofenamida [INN-Spanish]; 1,3-Disulfamyl-4,5-dichlorobenzene; Dasanide; Keveyis; Antidrasi; Dichlorphenamide [BAN]; Llorens Brand of Dichlorphenamide; Merck Brand of Dichlorphenamide; CB 8000; I7A; Daranide (TN); Dichlorophenamide (DCP); Dichlorphenamide (USP); Diclofenamide (JP15/INN); 3,4-Dichloro-5-sulfamylbenzenesulfonamide; 4,5-Dichloro-1,3-benzenedisulfonamide; 4,5-Dichloro-benzene-1,3-disulfonic acid diamide; 4,5-DICHLOROBENZENE-1,3-DISULFONAMIDE
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiglaucomic Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
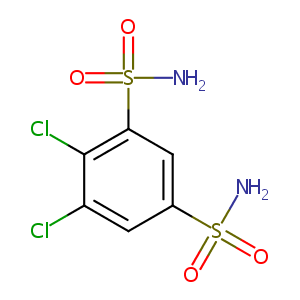 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 305.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 0.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Chronic glaucoma | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | 9C61.0Z | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Dichlorphenamide (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6807). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 3 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 4 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | ||||
| 5 | Product Information. Multaq (dronedarone). sanofi-aventis , Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 6 | Product Information. Savella (milnacipran). Forest Pharmaceuticals, St. Louis, MO. | ||||
| 7 | Product Information. Aptiom (eslicarbazepine). Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Marlborough, MA. | ||||
| 8 | Semple P, Tilstone WJ, Lawson DH "Furosemide and urinary digoxin clearance." N Engl J Med 293 (1975): 612-3. [PMID: 902451] | ||||
| 9 | Murphy BF, Whitworth JA, Kincaid-Smith P "Renal insufficiency with combinations of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and diuretics." Br Med J 288 (1984): 844-5. [PMID: 6322905] | ||||
| 10 | Ohnishi K, Yoshida H, Shigeno K, et al. "Prolongation of the QT interval and ventricular tachycardia in patients treated with arsenic trioxide for acute promyelocytic leukemia." Ann Intern Med 133 (2000): 881-5. [PMID: 11103058] | ||||
| 11 | Cohen J "Long-term efficacy and safety of terazosin alone and in combination with other antihypertensive agents." Am Heart J 122 (1991): 919-25. [PMID: 1678923] | ||||
| 12 | Cowan RA, Hartnell GG, Lowdell CP, Baird IM, Leak AM "Metabolic acidosis induced by carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and salicylates in patients with normal renal function." Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 289 (1984): 347-8. [PMID: 6432091] | ||||
