Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM13P4C)
| Drug Name |
Salsalate
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Diacesal; Diplosal; Disalcid; Disalicylsaeure; Disalyl; Nobacid; Salflex; Salical; Salina; Saloxium; Salsalato; Salsalatum;Salysal; Sasapirin; Sasapyrin; Sasapyrine; Sasapyrinum; Disalicylic acid; Sal Ester Sal; Salicylic Acid Salicylate; Salicyloylsalicylic acid; Salicylsalicylic acid; Disalcid (TN); O-Salicylcylsalicylsaeure; O-Salicyloylsalicylic Acid; O-Salicylsalicylic acid; Salflex (TN); Salicylic acid, bimolecular ester; Salicylic acid, salicylate; Salsalato [INN-Spanish]; Salsalatum [INN-Latin]; Salsitab (TN); Sasapyrine (JAN); Mono-Gesic (TN); Salsalate (USP/INN); Salsalate [USAN:INN:BAN]; Benzoic acid, 2-hydroxy-, 2-carboxyphenyl ester; 2-((2-Hydroxybenzoyl)oxy)benzoic acid; 2-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)oxybenzoic acid; 2-Carboxyphenyl salicylate; 2-Salicyloyloxybenzoic Acid; 2-{[(2-hydroxyphenyl)carbonyl]oxy}benzoic acid
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinflammatory Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
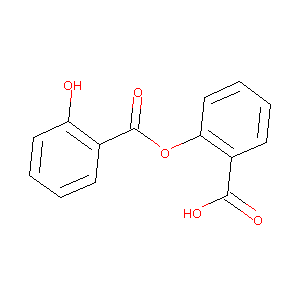 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 258.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Osteoarthritis | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | FA00-FA05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Salsalate (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
