Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMMAWLU)
| Drug Name |
Huperzine A
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Fordine; ( inverted exclamation markA)-Huperazine A; ( inverted exclamation markA)-Huperzine A; C15H18N2O; 5,9-Methanocycloocta(b)pyridin-2(1H)-one, 5-amino-11-ethylidene-5,6,9,10-tetrahydro-7-methyl-; rac-huperzine A; NCGC00159362-02; SCHEMBL679315; SCHEMBL1047469; CHEMBL394259; CHEBI:91724; MolPort-003-941-680
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
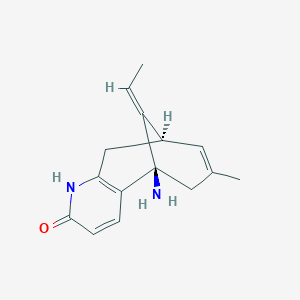 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 242.32 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Alzheimer disease | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | 8A20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
