Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMC8VNH)
| Drug Name |
Flufenamic Acid
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
flufenamic acid; 530-78-9; Fluphenamic acid; Nichisedan; Achless; Arlef; Tecramine; Paraflu; Lanceat; Flufacid; Plostene; Fullsafe; Parlef; Surika; Parlif; Flufenaminsaeure; Reumajust A; Acido flufenamico; N-(3-Trifluoromethylphenyl)anthranilic acid; Ristogen; Sastridex; Meralen; Ansatin; 2-((3-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl)amino)benzoic acid; Fluore-200; 2-{[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino}benzoic acid; ANT-1; Acide flufenamique; Acidum flufenamicum; TVX 916; INF 1837; 3'-Trifluoromethyldiphenylamine-2-carboxylic acid; NSC-82699; CI 440
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
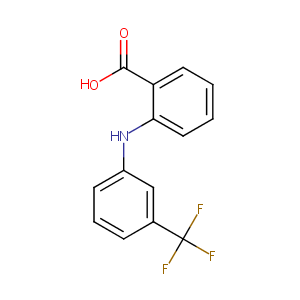 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 1 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 281.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 5.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Dysmenorrhea | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | GA34.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
