Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMG60ET)
| Drug Name |
GW-3965
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
GW3965; 405911-09-3; GW 3965; UNII-6JI5YOG7RC; GW-3965; 6JI5YOG7RC; CHEMBL59030; CHEBI:79995; (3-{3-[[2-CHLORO-3-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)BENZYL](2,2-DIPHENYLETHYL)AMINO]PROPOXY}PHENYL)ACETIC ACID; 2-[3-[3-[[2-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methyl-[2,2-di(phenyl)ethyl]amino]propoxy]phenyl]acetic acid; [3-(3-{[2-Chloro-3-(Trifluoromethyl)benzyl](2,2-Diphenylethyl)amino}propoxy)phenyl]acetic Acid; GW-3965A; 3-(3-[[2-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)(2,2-diphenylethyl)-amino]-propoxy}-phenyl acetic acid; GW 3965A
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
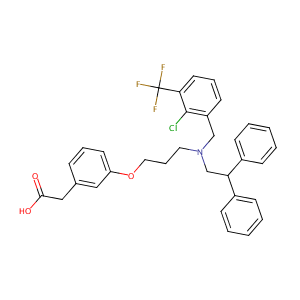 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 3 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 582 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 5.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
