Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMUZNIG)
| Drug Name |
Troleandomycin
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Aovine; Cyclamycin; Evramicina; Matromicina; Oleandocetin; Oleandocetine; TAO; Treolmicina; Triacetyloleandomycin; Triacetyloleandomycinum; Tribiocillina; Triocetin; Triolan; Troleandomicina; Troleandomycine; Troleandomycinum; Viamicina; Wytrion; Matromycin T; Oleandomycin triacetate; Oleandomycin triacetyl ester; Triacetyl ester of oleandomycin; WY 651; Tao (TN); Tao (VAN); Tekmisin (TN); Treis-Micina; Triacetyloleandomycin (JAN); Triocetin (TN); Troleandomicina [INN-Spanish]; Troleandomycin (TAO); Troleandomycin [USAN:INN]; Troleandomycine [INN-French]; Troleandomycinum [INN-Latin]; Oleandomycin, triacetate (ester); T.A.O; Troleandomycin (USP/INN); T.A.O.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antibiotics
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Enteric bacteria and other eubacteria
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
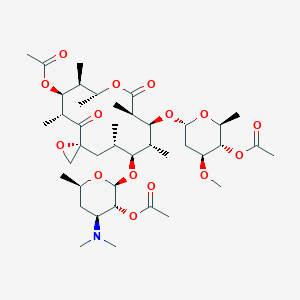 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL is unavailable | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 3 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 814 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 4.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Troleandomycin (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
