Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMSXKYG)
| Drug Name |
Gamma-Homolinolenic acid
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
DGLA; BML3-B11; Ro 12-1989; Star GLA (GNC); Bishomo-gamma-linolenic acid; C 20:3 n-6; Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid; Homo-gamma-linolenic acid; Homo-gamma-linolensaeure; Tona-lean 1000 CLA (Action Labs); Cis-8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic Acid; Eicosa-8Z,11Z,14Z-trienoic acid; All-cis-8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic acid; All-cis-8,11,14-icosatrienoic acid; All-cis-Eicosa-8,11,14-triensaeure; Cis,cis,cis-8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic acid; Cis-8,cis-11,cis-14-Eicosatrienoic acid; (8E,11E,14E)-8,11,14-Icosatrienoic acid; (8Z,11Z,14Z)-Icosatrienoic acid; (8Z,11Z,14Z)-icosa-8,11,14-trienoic acid; (Z,Z,Z)-8,11,14-Eicosatrienoate; (Z,Z,Z)-8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic acid; (Z,Z,Z)-8,11,14-Icosatrienoate; (Z,Z,Z)-8,11,14-Icosatrienoicacid; 20:3, n-6,9,12 all-cis; 8, 11, 14-eicosatrienoic acid; 8,11,14-Eicosatrienoate; 8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic acid; 8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic acid, (8Z,11Z,14Z)-(9CI); 8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic acid, (Z,Z,Z)-(8CI); 8,11,14-Icosatrienoate; 8,11,14-all-cis-Eicosatrienoic acid; 8c,11c,14c-Eicosatriensaeure; 8c,11c,14c-eicosatrienoic acid
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Dietary supplement
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
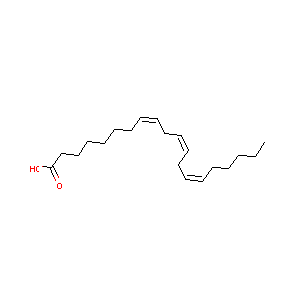 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 2 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 306.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 7.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Malnutrition | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | 5B50-5B71 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
