Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM2R86O)
| Drug Name |
Siponimod
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | BAF312 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
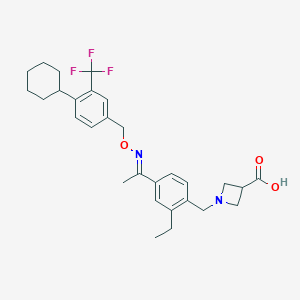 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 1 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 516.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 4.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| ICD Disease Classification | 08 Nervous system disease | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease Class | ICD-11: 8A40 Multiple sclerosis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The Studied Tissue | Plasmacytoid dendritic cells | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The Studied Disease | Multiple sclerosis [ICD-11:8A40] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Siponimod
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Siponimod (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health Human Services. 2019 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01665144) Exploring the Efficacy and Safety of Siponimod in Patients With Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis (EXPAND). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | ||||
| 3 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | ||||
| 4 | Metabolism and disposition of siponimod, a novel selective S1P1/S1P5 agonist, in healthy volunteers and in vitro identification of human cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in its oxidative metabolism. Drug Metab Dispos. 2018 Jul;46(7):1001-1013. | ||||
| 5 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 6 | Product Information. Arcapta Neohaler (indacaterol). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
