Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMY2AH1)
| Drug Name |
Aminophenazone
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
AMINOPYRINE; Amidazofen; Amidazophen; Amidazophene; Amidofebrin; Amidofen; Amidophen; Amidophenazone; Amidopyrazoline; Amidopyrin; Amidopyrine; Aminofenazone; Aminophenazon; Aminopyrin; Anafebrina; Brufaneuxol; Dereuma; Dimapyrin; Dimethylaminoantipyrine; Dimethylaminoazophene; Dimethylaminophenazone; Dipirin; Dipyrin; Dipyrine; Eufibron; Febrinina; Febron; Hyparon; Itamidone; Mamallet-A; Novamidon; Piramidon; Pirazon; Piridol; Piromidina; Polinalin; Pyradone; Pyramidon; Pyramidone; aminophenazone; 4-Dimethylaminoantipyrine; 58-15-1
|
|||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||
| ATC Code | ||||||
| Structure |
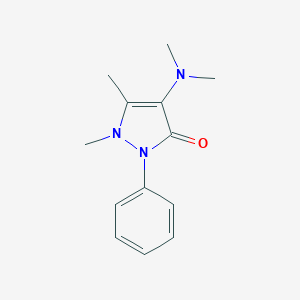 |
|||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 231.29 | ||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 1 | |||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 2 | |||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 0 | |||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 3 | |||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
