| 1 |
Recurrent recessive mutation in deoxyguanosine kinase causes idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension.Hepatology. 2016 Jun;63(6):1977-86. doi: 10.1002/hep.28499. Epub 2016 Mar 31.
|
| 2 |
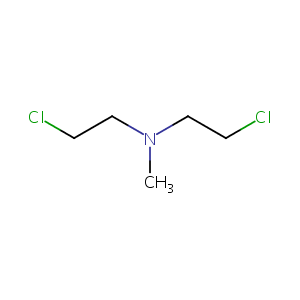
Mechlorethamine FDA Label
|
| 3 |
Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015
|
| 4 |
URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7218).
|
| 5 |
Busulfan FDA Label
|
| 6 |
URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7136).
|
| 7 |
Thioredoxin Cross-Linking by Nitrogen Mustard in Lung Epithelial Cells: Formation of Multimeric Thioredoxin/Thioredoxin Reductase Complexes and Inhibition of Disulfide Reduction. Chem Res Toxicol. 2015 Nov 16;28(11):2091-103. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00194. Epub 2015 Oct 19.
|
| 8 |
Cross-linking of thioredoxin reductase by the sulfur mustard analogue mechlorethamine (methylbis(2-chloroethyl)amine) in human lung epithelial cells and rat lung: selective inhibition of disulfide reduction but not redox cycling. Chem Res Toxicol. 2014 Jan 21;27(1):61-75. doi: 10.1021/tx400329a. Epub 2013 Dec 9.
|
| 9 |
Proteomic analysis of DNA-protein cross-linking by antitumor nitrogen mustards. Chem Res Toxicol. 2009 Jun;22(6):1151-62.
|
| 10 |
Down-regulation of HER-2 expression in human breast cancer cell HBC-4 and ZR75-1 by nitrogen-mustard-N-oxide. Kobe J Med Sci. 2007;53(4):135-42.
|
| 11 |
Nitrogen Mustard Alkylates and Cross-Links p53 in Human Keratinocytes. Chem Res Toxicol. 2022 Apr 18;35(4):636-650. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.1c00420. Epub 2022 Mar 21.
|
| 12 |
Nitrogen mustard prevents transport of Fra-1 into the nucleus to promote c-Fos- and FosB-dependent IL-8 induction in injured mouse epidermis. Toxicol Lett. 2020 Feb 1;319:256-263. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.10.006. Epub 2019 Oct 19.
|
| 13 |
G2 delay induced by nitrogen mustard in human cells affects cyclin A/cdk2 and cyclin B1/cdc2-kinase complexes differently. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8298-308.
|
| 14 |
Overexpression of GSTA2 protects against cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induced by the DNA inter-strand crosslinking nitrogen mustard, mechlorethamine. J Cell Biochem. 2005 May 15;95(2):339-51. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20440.
|
| 15 |
Inhibition of caspase-dependent mitochondrial permeability transition protects airway epithelial cells against mustard-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis. 2006 Sep;11(9):1545-59. doi: 10.1007/s10495-006-8764-1.
|
| 16 |
S100P is selectively upregulated in tumor cell lines challenged with DNA cross-linking agents. Leuk Res. 2005 Oct;29(10):1181-90. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2005.03.012.
|
| 17 |
Ebselen reduces the toxicity of mechlorethamine in A-431 cells via inhibition of apoptosis. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2013 Jun;27(6):313-22. doi: 10.1002/jbt.21490. Epub 2013 May 6.
|
| 18 |
Histopathologic and immunohistochemical features in human skin after exposure to nitrogen and sulfur mustard. Am J Dermatopathol. 1998 Feb;20(1):22-8. doi: 10.1097/00000372-199802000-00005.
|
| 19 |
Increased expression of VDAC1 sensitizes carcinoma cells to apoptosis induced by DNA cross-linking agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 May 1;83(9):1172-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.01.017. Epub 2012 Jan 21.
|
| 20 |
Activation of the human TRPA1 channel by different alkylating sulfur and nitrogen mustards and structurally related chemotherapeutic drugs. Toxicol Lett. 2023 Mar 1;376:51-59. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2023.01.007. Epub 2023 Jan 21.
|
| 21 |
Direct transcriptomic comparison of xenobiotic metabolism and toxicity pathway induction of airway epithelium models at an air-liquid interface generated from induced pluripotent stem cells and primary bronchial epithelial cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023 Feb;39(1):1-18. doi: 10.1007/s10565-022-09726-0. Epub 2022 May 31.
|
| 22 |
DNA intrastrand cross-link at the 5'-GA-3' sequence formed by busulfan and its role in the cytotoxic effect. Cancer Sci. 2004 May;95(5):454-8.
|
| 23 |
Update: clinically significant cytochrome P-450 drug interactions. Pharmacotherapy. 1998 Jan-Feb;18(1):84-112.
|
| 24 |
Glutathione S-transferase M1 polymorphism: a risk factor for hepatic venoocclusive disease in bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 2004 Sep 1;104(5):1574-7.
|
| 25 |
Endothelial cells do not express GSTA1: potential relevance to busulfan-mediated endothelial damage during haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Eur J Haematol. 2008 Apr;80(4):299-302.
|
| 26 |
Busulfan conjugation by glutathione S-transferases alpha, mu, and pi. Drug Metab Dispos. 1996 Sep;24(9):1015-9.
|
| 27 |
Overexpression of glutathione-S-transferase, MGSTII, confers resistance to busulfan and melphalan. Cancer Invest. 2005;23(1):19-25.
|
| 28 |
Influence of glutathione S-transferase A1, P1, M1, T1 polymorphisms on oral busulfan pharmacokinetics in children with congenital hemoglobinopathies undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2010 Dec 1;55(6):1172-9. doi: 10.1002/pbc.22739.
|
| 29 |
Overexpression of glutathione S-transferase A1-1 in ECV 304 cells protects against busulfan mediated G2-arrest and induces tissue factor expression. Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Dec;137(7):1100-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704972.
|
| 30 |
Busulfan induces activin A expression in vitro and in vivo: a possible link to venous occlusive disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003 Sep;74(3):264-74.
|
| 31 |
Decreased incidence of hepatic veno-occlusive disease and fewer hemostatic derangements associated with intravenous busulfan vs oral busulfan in adults conditioned with busulfan + cyclophosphamide for allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Ann Hematol. 2005 May;84(5):321-30. doi: 10.1007/s00277-004-0982-4. Epub 2004 Dec 4.
|
| 32 |
Antineoplastic agent busulfan regulates a network of genes related to coagulation and fibrinolysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Jun;68(6):923-35. doi: 10.1007/s00228-011-1209-y.
|
| 33 |
Association of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 inhibition in in vitro assays with drug-induced liver injury. J Toxicol Sci. 2021;46(4):167-176. doi: 10.2131/jts.46.167.
|
| 34 |
Altered gene expression in busulfan-resistant human myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 2008 Nov;32(11):1684-97. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2008.01.016. Epub 2008 Mar 12.
|
| 35 |
Busulfan selectively induces cellular senescence but not apoptosis in WI38 fibroblasts via a p53-independent but extracellular signal-regulated kinase-p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mechanism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Nov;319(2):551-60. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.107771. Epub 2006 Aug 1.
|
| 36 |
Reduced expression of Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor-alpha modulates the cytotoxic effect of busulfan in HEK293 cells. Anticancer Drugs. 2007 Mar;18(3):333-40. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e328011fd7f.
|
| 37 |
CD34+ derived macrophage and dendritic cells display differential responses to paraquat. Toxicol In Vitro. 2021 Sep;75:105198. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2021.105198. Epub 2021 Jun 9.
|
| 38 |
Impairment of APE1 function enhances cellular sensitivity to clinically relevant alkylators and antimetabolites. Mol Cancer Res. 2009 Jun;7(6):897-906. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0519. Epub 2009 May 26.
|
| 39 |
Loss of function mutations in VARS encoding cytoplasmic valyl-tRNA synthetase cause microcephaly, seizures, and progressive cerebral atrophy.Hum Genet. 2018 Apr;137(4):293-303. doi: 10.1007/s00439-018-1882-3. Epub 2018 Apr 24.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|