Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMGCHDS)
| Drug Name |
Sulfamethizole
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ayerlucil; Famet; Lucosil; Methazol; Microsul; Proklar; Renasul; Rufol; SULFAMETHIAZOLE; Salimol; Solfametizolo; Sulamethizole; Sulfamethazole; Sulfamethizol; Sulfamethizolum; Sulfamethylthiadiazole; Sulfametizol; Sulfapyelon; Sulfstat; Sulfurine; Sulphamethizole; Sulphamethyltiadiazole; Tetracid; Thidicur;Thiosulfil; Ultrasul; Urocydal; Urodiaton; Urolucosil; Urosulfin; Uroz; Solfametizolo [DCIT]; Sulfa gram; Thiosulfil Forte; RP 2145; VK 53; Sulfamethizolum [INN-Latin]; Sulfametizol [INN-Spanish]; Thiosulfil (TN); Sulfamethizole [USAN:INN:JAN]; Thiosulfil-A-Forte; Sulfamethizole (JP15/USP/INN); N1-(5-Methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)sulfanilamide; N(1)-(5-Methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)sulfanilamide; N(sup 1)-(5-Methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)sulfanilamide; N(sup 1)-(5-Methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)-sulfanilamide; 2-(p-Aminobenzenesulfonamido)-5-methylthiadiazole; 2-Methyl-5-sulfanilamido-1,3,4-thiadiazole; 2-Sulfanilamido-5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole; 4-Amino-N-(5-Methyl-1,3,4-Thiadiazol-2-Yl)Benzene-1-Sulfonamide; 4-Amino-N-(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide; 4-Amino-N-[5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]benzenesulfonamide; 5-Methyl-2-sulfanilamido-1,3,4-thiadiazole
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinfective Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Enteric bacteria and other eubacteria
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
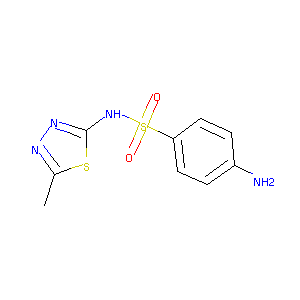 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 270.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 0.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Sulfamethizole (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
