Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMPHZQE)
| Drug Name |
Chlorpropamide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Adiaben; Asucrol; Bioglumin; Catanil; Chlorodiabina; Chloronase; Chloropropamide; Chlorporpamide; Chlorpropamid; Chlorpropamidum; Clorpropamid; Clorpropamida; Clorpropamide; Diabaril; Diabechlor; Diabenal; Diabenese; Diabeneza; Diabetoral; Diabexan; Diabinese; Dynalase; Glisema; Glucamide; Insogen; Insulase; Meldian; Melitase; Mellinese; Millinese; Oradian; Prodiaben; Stabinol; Apotex Brand of Chlorpropamide; Byk Gulden Brand of Chlorpropamide; CHLORPROPAMIDE USP; Clorpropamide [DCIT]; Clorpropamide [Italian];Dia benese; Diamel Ex; Farmasierra Brand of Chlorpropamide; Pfizer Brand of Chlorpropamide; C 1290; P 607; Apo-Chlorpropamide; Chlorpropamide Bp/ Usp; Chlorpropamidum [INN-Latin]; Clorpropamida [INN-Spanish]; Diabet-Pages; Diabinese (TN); Novo-Propamide; U-3818; U-9818; Chlorpropamide [INN:BAN:JAN]; Chlorpropamide (JP15/USP/INN); N3-Butyl-N1-p-chlorobenzenesulfonylure a; N3-Butyl-N1-p-chlorobenzenesulfonylurea; N-Propyl-N'-p-chlorophenylsulfonylcarbamide; N-Propyl-N'-p-chlorphenylsulfonylcarbamide; N-propyl-N'-p-chlorophenylsu lfonylcarbamide; N-(4-Chlorophenylsulfonyl)-N'-propylurea; N-(p-Chlorobenzenesulfonyl)-N'-propylurea; N-Propyl-N'-(p-chlorobenzenesulfonyl)urea; 1-((p-Chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3-propylurea; 1-(4-Chlorophenylsulfonyl)-3-propylurea; 1-(4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl-3-propylurea; 1-(p-Chlorobenzenesulfonyl)-3-propylurea; 1-(p-Chlorobenzensulfonyl)-3-propylurea; 1-(p-Chlorophenylsulfonyl)-3-propylurea; 1-(para-Chlorophenylsulfonyl)-3-propylurea; 1-Propyl-3-(p-chlorobenzenesulfonyl)urea; 1-[(4-chlorobenzene)sulfonyl]-3-propylurea; 1-[p-Chlorobenzenesulfonyl]-3-propylurea; 1-p-Chlorophenyl-3-(propylsulfonyl)urea; 4-Chloro-4-((propylamino)carbonyl)benzenesulfonamide; 4-Chloro-N-((propylamino)carbonyl)benzenesulfonamide; 4-chloro-N-(propylcarbamoyl)benzenesulfonamide; 4-chloro-N-[(propylamino)carbonyl]benzenesulfonamide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Hypoglycemic Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
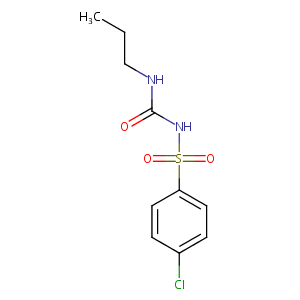 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 276.74 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 2.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Chlorpropamide (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6801). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Critical Evaluation of Human Oral Bioavailability for Pharmaceutical Drugs by Using Various Cheminformatics Approaches | ||||
| 3 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 6 | Effect of the chlorpropamide and fructose-1,6-bisphosphate of soluble TNF receptor II levels. Pharmacol Res. 2004 May;49(5):449-53. | ||||
| 7 | Chlorpropamide 2-hydroxylation is catalysed by CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 in vitro: chlorpropamide disposition is influenced by CYP2C9, but not by CYP2C19 genetic polymorphism. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005 May;59(5):552-63. | ||||
| 8 | Effect of common medications on the expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry receptors in liver tissue. Arch Toxicol. 2020 Dec;94(12):4037-4041. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02869-1. Epub 2020 Aug 17. | ||||
| 9 | Effects of prolonged in vitro exposure to sulphonylureas on the function and survival of human islets. J Diabetes Complications. 2005 Jan-Feb;19(1):60-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2004.05.001. | ||||
| 10 | Selection of drugs to test the specificity of the Tg.AC assay by screening for induction of the gadd153 promoter in vitro. Toxicol Sci. 2003 Aug;74(2):260-70. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfg113. Epub 2003 May 2. | ||||
| 11 | Inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone induced by chlorpropamide. Am J Med Sci. 1972 Mar;263(3):137-41. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197203000-00002. | ||||
| 12 | Kivisto KT, Neuvonen PJ "Effect of magnesium hydroxide on the absorption and efficacy of tolbutamide and chlorpropamide." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 42 (1992): 675-80. [PMID: 1623912] | ||||
| 13 | Kivisto KT, Neuvonen PJ "Differential effects of sodium bicarbonate and aluminium hydroxide on the absorption and activity of glipizide." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 40 (1991): 383-6. [PMID: 1646724] | ||||
| 14 | Product Information. Starlix (nateglinide) Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 15 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 16 | Christensen LK, Hansen JM, Kristensen M "Sulphaphenazole-induced hypoglycemic attacks in tolbutamide-treated diabetics." Lancet 2 (1963): 1298-301. [PMID: 14071924] | ||||
| 17 | Product Information. Piqray (alpelisib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 18 | Abad S, Moachon L, Blanche P, Bavoux F, Sicard D, Salmon-Ceron D "Possible interaction between glicazide, fluconazole and sulfamethoxazole resulting in severe hypoglycaemia." Br J Clin Pharmacol 52 (2001): 456-7. [PMID: 11678792] | ||||
| 19 | Mahfouz M, Abdel-Maguid R, El-Dakhakhny M "Potentiation of the hypoglycaemic action of tolbutamide by different drugs." Arzneimittelforschung 20 (1970): 120-2. [PMID: 5467602] | ||||
| 20 | Hansen JM, Christensen LK "Drug interactions with oral sulphonylurea hypoglycaemic drugs." Drugs 13 (1977): 24-34. [PMID: 401727] | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Korlym (mifepristone). Corcept Therapeutics Incorporated, Menlo Park, CA. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Kalydeco (ivacaftor). Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Prevymis (letermovir). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 24 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 25 | Borcherding SM, Baciewicz AM, Self TH "Update on rifampin drug interactions." Arch Intern Med 152 (1992): 711-6. [PMID: 1558427] | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Priftin (rifapentine). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 28 | Gachalyi B, Tornyossy, Vas A, Kaldor A "Effect of alphamethyldopa on the half-lives of antipyrine, tolbutamide and D-glucaric acid excretion in man." Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 18 (1980): 133-5. [PMID: 6103880] | ||||
| 29 | Blakely KM, Drucker AM, Rosen CF "Drug-induced photosensitivity-an update: Culprit drugs, prevention and management." Drug Saf 42 (2019): 827-47. [PMID: 30888626] | ||||
| 30 | EMA. European Medicines Agency. European Union "EMA - List of medicines under additional monitoring.". | ||||
| 31 | Dey NG, Castleden CM, Ward J, et al "The effect of cimetidine on tolbutamide kinetics." Br J Clin Pharmacol 16 (1983): 438-40. [PMID: 6626438] | ||||
| 32 | Humphries TJ "Clinical implications of drug interactions with the cytochrome P-450 enzyme system associated with omeprazole." Dig Dis Sci 36 (1991): 1665-9. [PMID: 1748033] | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Zokinvy (lonafarnib). Eiger BioPharmaceuticals, Palo Alto, CA. | ||||
| 34 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Arava (leflunomide). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
