Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM8JXPZ)
| Drug Name |
Glibenclamide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Abbenclamide; Adiab; Azuglucon; Bastiverit; Benclamin; Betanase; Calabren; Cytagon; Daonil; Debtan; Diabeta; Diabiphage; Dibelet; Duraglucon; Euclamin; Euglucan; Euglucon; Euglykon; Gewaglucon; Gilemal; Glamide; Glibadone; Gliban; Gliben; Glibenbeta; Glibenclamida; Glibenclamidum; Glibenil; Glibens; Glibesyn; Glibet; Glibetic; Glibil; Gliboral; Glicem; Glidiabet; Glimel; Glimide; Glimidstata; Glisulin; Glitisol; Glubate; Gluben; Glucobene; Glucohexal; Glucolon; Glucomid; Glucoremed; Glucoven; Glyben; Glybenclamide; Glybenzcyclamide; Glyburide; Glycolande; Glycomin; Glynase; Hexaglucon; Humedia; Lederglib; Libanil; Lisaglucon; Maninil; Melix; Micronase; Miglucan; Nadib; Neogluconin; Normoglucon; Orabetic; Pira; Praeciglucon; PresTab; Prodiabet; Renabetic; Sugril; Suraben; Tiabet; Yuglucon; Euglucon N; Glibenclamid AL; Glibenclamid Basics; Glibenclamid Fabra; Glibenclamid Genericon; Glibenclamid Heumann; Glibenclamid Riker M; Glyburide [USAN]; Micronized glyburide; Betanese 5; Euglucon 5; G 0639; GBN 5; HB 419; HB 420; HB419; HB420; Norglicem 5; U 26452; UR 606; Apo-Glibenclamide; Daonil (TN); Dia-basan; Diabeta (TN); Euglucon (TN); Gen-Glybe; Gliben-Puren N; Glibenclamid Riker M.; Glibenclamid-Cophar; Glibenclamid-Ratiopharm; Glibenclamida [INN-Spanish]; Glibenclamidum [INN-Latin]; Gluco-Tablimen; Glyburide (USP); Glyburide (micronized); Glynase (TN); HB-419; HB-420; Hemi-Daonil; Med-Glionil; Micronase (TN); Novo-Glyburide; Semi-Euglucon; Semi-daonil; U-26452; Glibenclamide (JP15/INN); Semi-Daonil (TN); Semi-Gliben-Puren N; N-p-[2-(5-Chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl]benzenesulfonyl-N'-cyclohexylurea; N-p-[2-(5-Chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)-ethyl]benzene-sulfonyl-N-cyclohexylurea; N-(4-(2-(5-Chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl)phenylsulfonyl)-N'-cyclohexylurea; 1-((p-(2-(5-Chloro-o-anisamido)ethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)-3-cyclohexylurea; 1-(p-(2-(5-Chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl)benzenesulfonyl)-3-cyclohexylurea; 5-Chloro-N-[4-(cyclohexylureidosulfonyl)phenethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide; 5-chloro-N-[2-[4-(cyclohexylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]ethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Hypoglycemic Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
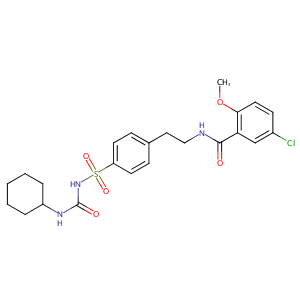 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 494 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 4.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Experimental Cancer Drug Sensitivity Information
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Glibenclamide (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
| DIG |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Formulation |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2414). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Spectroscopic interactions of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus with levocetirizine. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2021 Jul;34(4(Supplementary)):1639-1644. | ||||
| 3 | Antibodies and venom peptides: new modalities for ion channels. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019 May;18(5):339-357. | ||||
| 4 | Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of glyburide in young and elderly patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Ann Pharmacother. 1996 May;30(5):472-5. doi: 10.1177/106002809603000507. | ||||
| 5 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 6 | Critical Evaluation of Human Oral Bioavailability for Pharmaceutical Drugs by Using Various Cheminformatics Approaches | ||||
| 7 | FDA Approved Drug Products: Glynase (Glyburide) Oral Tablets | ||||
| 8 | Silberstein SD, McCrory DC: Butalbital in the treatment of headache: history, pharmacology, and efficacy. Headache. 2001 Nov-Dec;41(10):953-67. | ||||
| 9 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 10 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 11 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 12 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 13 | Transport of glyburide by placental ABC transporters: implications in fetal drug exposure. Placenta. 2006 Nov-Dec;27(11-12):1096-102. | ||||
| 14 | Citrus juices inhibit the function of human organic anion-transporting polypeptide OATP-B. Drug Metab Dispos. 2005 Apr;33(4):518-23. | ||||
| 15 | Glyburide transport across the human placenta. Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Mar;125(3):583-8. | ||||
| 16 | Substrates, inducers, inhibitors and structure-activity relationships of human Cytochrome P450 2C9 and implications in drug development. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(27):3480-675. | ||||
| 17 | Contributions of human cytochrome P450 enzymes to glyburide metabolism. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2010 May;31(4):228-42. | ||||
| 18 | Contribution of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases 1A9 and 2B7 to the glucuronidation of indomethacin in the human liver. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2007 Mar;63(3):289-96. | ||||
| 19 | Identification of CYP3A7 for glyburide metabolism in human fetal livers. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Dec 15;92(4):690-700. | ||||
| 20 | Chromatographic studies of changes in binding of sulfonylurea drugs to human serum albumin due to glycation and fatty acids. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2010 Nov 15;878(30):3193-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2010.09.033. Epub 2010 Oct 23. | ||||
| 21 | Initro inhibition of AKR1Cs by sulphonylureas and the structural basis. Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Oct 5;240:310-5. | ||||
| 22 | Effect of common medications on the expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry receptors in liver tissue. Arch Toxicol. 2020 Dec;94(12):4037-4041. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02869-1. Epub 2020 Aug 17. | ||||
| 23 | The intermediate conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel inhibitor TRAM-34 stimulates proliferation of breast cancer cells via activation of oestrogen receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Feb 1;159(3):650-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00557.x. Epub 2009 Dec 24. | ||||
| 24 | Potential cholestatic activity of various therapeutic agents assessed by bile canalicular membrane vesicles isolated from rats and humans. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2003;18(1):16-22. | ||||
| 25 | A potential role of calpains in sulfonylureas (SUs) -mediated death of human pancreatic cancer cells (1.2B4). Toxicol In Vitro. 2021 Jun;73:105128. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2021.105128. Epub 2021 Feb 27. | ||||
| 26 | Kivisto KT, Neuvonen PJ "Effect of magnesium hydroxide on the absorption and efficacy of tolbutamide and chlorpropamide." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 42 (1992): 675-80. [PMID: 1623912] | ||||
| 27 | Kivisto KT, Neuvonen PJ "Differential effects of sodium bicarbonate and aluminium hydroxide on the absorption and activity of glipizide." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 40 (1991): 383-6. [PMID: 1646724] | ||||
| 28 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 29 | Abad S, Moachon L, Blanche P, Bavoux F, Sicard D, Salmon-Ceron D "Possible interaction between glicazide, fluconazole and sulfamethoxazole resulting in severe hypoglycaemia." Br J Clin Pharmacol 52 (2001): 456-7. [PMID: 11678792] | ||||
| 30 | Bussing R, Gende A "Severe hypoglycemia from clarithromycin-sulfonylurea drug interaction." Diabetes Care 25 (2002): 1659-61. [PMID: 12196446] | ||||
| 31 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Piqray (alpelisib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 33 | Hansen JM, Christensen LK "Drug interactions with oral sulphonylurea hypoglycaemic drugs." Drugs 13 (1977): 24-34. [PMID: 401727] | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Kalydeco (ivacaftor). Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Prevymis (letermovir). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 36 | Borcherding SM, Baciewicz AM, Self TH "Update on rifampin drug interactions." Arch Intern Med 152 (1992): 711-6. [PMID: 1558427] | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Priftin (rifapentine). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 38 | Product Information. Rukobia (fostemsavir). ViiV Healthcare, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Nexletol (bempedoic acid). Esperion Therapeutics, Ann Arbor, MI. | ||||
| 41 | Appel S, Rufenacht T, Kalafsky G, et al. "Lack of interaction between fluvastatin and oral hypoglycemic agents in healthy subjects and in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus." Am J Cardiol 76 (1995): a29-32. [PMID: 7604792] | ||||
| 42 | EMA. European Medicines Agency. European Union "EMA - List of medicines under additional monitoring.". | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 44 | Product Information. Fycompa (perampanel). Eisai Inc, Teaneck, NJ. | ||||
| 45 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 46 | Product Information. Arava (leflunomide). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 47 | Allred AJ, Bowen CJ, Park JW, et al. "Eltrombopag increases plasma rosuvastatin exposure in healthy volunteers." Br J Clin Pharmacol 72 (2011): 321-9. [PMID: 21434975] | ||||
