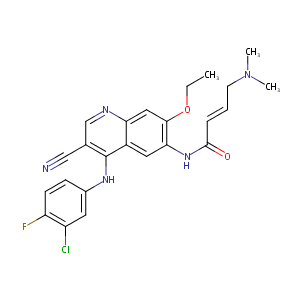
| DOT Name |
DOT ID |
UniProt ID |
Mode of Action |
REF |
|
Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta (IKBKB)
|
OT9RDS3H
|
IKKB_HUMAN
|
Decreases Expression
|
[6] |
|
Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 5 (BIRC5)
|
OTILXZYL
|
BIRC5_HUMAN
|
Decreases Expression
|
[6] |
|
B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 10 (BCL10)
|
OT47MCLI
|
BCL10_HUMAN
|
Decreases Expression
|
[6] |
|
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)
|
OTAPLO1S
|
EGFR_HUMAN
|
Decreases Activity
|
[7] |
|
Transcription factor Sp1 (SP1)
|
OTISPT4X
|
SP1_HUMAN
|
Decreases Activity
|
[6] |
|
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2)
|
OT9DVHC0
|
BCL2_HUMAN
|
Decreases Expression
|
[6] |
|
Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-1 (ATF1)
|
OT251CI0
|
ATF1_HUMAN
|
Decreases Expression
|
[6] |
|
B-cell lymphoma 3 protein (BCL3)
|
OT1M5B95
|
BCL3_HUMAN
|
Decreases Expression
|
[6] |
|
NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha (NFKBIA)
|
OTFT924M
|
IKBA_HUMAN
|
Increases Expression
|
[6] |
|
RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1)
|
OT8H2YY7
|
AKT1_HUMAN
|
Decreases Expression
|
[6] |
|
Apoptosis regulator BAX (BAX)
|
OTAW0V4V
|
BAX_HUMAN
|
Increases Expression
|
[6] |
|
Bcl-2-like protein 1 (BCL2L1)
|
OTRC5K9O
|
B2CL1_HUMAN
|
Decreases Expression
|
[6] |
|
Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 1 (NAIP)
|
OTLA925F
|
BIRC1_HUMAN
|
Decreases Expression
|
[6] |
|
Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 2 (BIRC2)
|
OTFXFREP
|
BIRC2_HUMAN
|
Decreases Expression
|
[6] |
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
|
|
|