Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMCL2OK)
| Drug Name |
Disulfiram
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Abstenisil; Abstinil; Abstinyl; Alcophobin; Antabus; Antabuse; Antadix; Antaenyl; Antaethan; Antaethyl; Antaetil; Antalcol; Antetan; Antethyl; Antetil; Anteyl; Anthethyl; Antiaethan; Anticol; Antietanol; Antiethanol; Antietil; Antikol; Antivitium; Aversan; Averzan; Bonibal; Contralin; Contrapot; Cronetal; Dicupral; Disetil; Disulfan; Disulfirame; Disulfiramo; Disulfiramum; Disulfirm; Disulfram; Disulfuram; Disulphuram; Ephorran; Espenal; Esperal; Etabus; Ethyldithiourame; Ethyldithiurame; Exhoran; Exhorran; Gababentin; Hoca; Krotenal; Nocbin; Nocceler; Noxal; Refusal; Stopaethyl; Stopethyl; Stopety; Stopetyl; TATD; TETD; THIOCID; TTD; TTS; Tenurid; Tenutex; Tetidis; Tetradin; Tetradine; Tetraethylthiuram; Tetraetil; Teturam; Teturamin; Thireranide; Thiuranide; Tillram; Tiuram; Accel TET; Akrochem TETD; Ancazide ET; Antab use; Disulfirame [DCIT]; Ekagom DTET; Ekagom TEDS; Ekagom TETDS; Ekaland TETD; Esperal [France]; Eta bus; Ethyl Thiram; Ethyl Thiudad; Ethyl Thiurad; Ethyl Tuads Rodform; Ethyl Tuex; Ethyl tuads; Etyl Tuex; Nocceler TET; Perkacit TETD; Perkait TETD; Robac TET; Sanceler TET; Soxinol TET; TTS x; Tet raethylthiuram; Thiuram E; Dupon 4472; T 1132; Accel TET-R; Alk-aubs; Antabus (TN); Antabuse (TN); Anti-ethyl; Antivitium (Spain); ENT 27,340; Nocceler TET-G; Noxal (VAN); Ro-sulfiram; Sanceler TET-G; Tuads, ethyl; Usaf B-33; Ro-Sulfram-500 (USA)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Alcohol Deterrents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
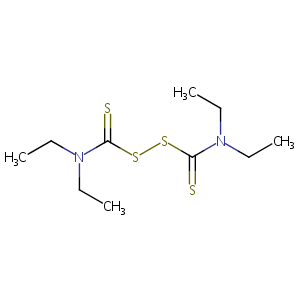 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 296.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 3.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Disulfiram (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Structure of Mpro from COVID-19 virus and discovery of its inhibitors. Nature. 2020 Apr 9. | ||||
| 3 | Therapeutic options for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020 Mar;19(3):149-150. | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Critical Evaluation of Human Oral Bioavailability for Pharmaceutical Drugs by Using Various Cheminformatics Approaches | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 8 | Pharmacological treatment of alcohol dependence: target symptoms and target mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Sep;111(3):855-76. | ||||
| 9 | Interaction of disulfiram with antiretroviral medications: efavirenz increases while atazanavir decreases disulfiram effect on enzymes of alcohol metabolism. Am J Addict. 2014 Mar-Apr;23(2):137-44. | ||||
| 10 | Duration of cytochrome P-450 2E1 (CYP2E1) inhibition and estimation of functional CYP2E1 enzyme half-life after single-dose disulfiram administration in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Oct;291(1):213-9. | ||||
| 11 | Identification of the human P-450 enzymes responsible for the sulfoxidation and thiono-oxidation of diethyldithiocarbamate methyl ester: role of P-450 enzymes in disulfiram bioactivation. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998 Sep;22(6):1212-9. | ||||
| 12 | Species-specific differences in the inhibition of human and zebrafish 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 by thiram and organotins. Toxicology. 2012 Nov 15;301(1-3):72-8. | ||||
| 13 | Keratinocyte gene expression profiles discriminate sensitizing and irritating compounds. Toxicol Sci. 2010 Sep;117(1):81-9. | ||||
| 14 | Disulfiram suppresses invasive ability of osteosarcoma cells via the inhibition of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Nov 30;40(6):1069-76. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2007.40.6.1069. | ||||
| 15 | The interaction of disulfiram and H(2)S metabolism in inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase activity and liver cancer cell growth. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 1;426:115642. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2021.115642. Epub 2021 Jul 6. | ||||
| 16 | Contribution of aldehyde dehydrogenase 3A1 to disulfiram penetration through monolayers consisting of cultured human corneal epithelial cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jul;31(7):1444-8. doi: 10.1248/bpb.31.1444. | ||||
| 17 | The enzymatic activity of human aldehyde dehydrogenases 1A2 and 2 (ALDH1A2 and ALDH2) is detected by Aldefluor, inhibited by diethylaminobenzaldehyde and has significant effects on cell proliferation and drug resistance. Chem Biol Interact. 2012 Jan 5;195(1):52-60. | ||||
| 18 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 19 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 20 | Loi CM, Day JD, Jue SG, et al "Dose-dependent inhibition of theophylline metabolism by disulfiram in recovering alcoholics." Clin Pharmacol Ther 45 (1989): 476-86. [PMID: 2721103] | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Antabuse (disulfiram). Wyeth-Ayerst Laboratories, Philadelphia, PA. | ||||
| 23 | Brown CG, Kaminsky MJ, Feroli ER, Gurley HT "Delirium with phenytoin and disulfiram administration." Ann Emerg Med 12 (1983): 310-3. [PMID: 6625283] | ||||
| 24 | Whittington HG, Grey L "Possible interaction between disulfiram and isoniazid." Am J Psychiatry 125 (1969): 1725-9. [PMID: 5770196] | ||||
| 25 | Carrion C, Espinosa E, Herrero A, Garcia B "Possible vincristine-isoniazid interaction." Ann Pharmacother 29 (1995): 201. [PMID: 7756727] | ||||
| 26 | Elenbaas RM "Drug therapy reviews: management of the disulfiram-alcohol reaction." Am J Hosp Pharm 34 (1977): 827-31. [PMID: 331944] | ||||
| 27 | Argov Z, Mastaglia FL "Drug-induced peripheral neuropathies." Br Med J 1 (1979): 663-6. [PMID: 219931] | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Ziagen (abacavir). Glaxo Wellcome, Research Triangle Pk, NC. | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 30 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 32 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 33 | Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et.al "Successful treatment of l-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors." Leuk Lymphoma 55 (2014): 1670-4. [PMID: 24090500] | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Levitra (vardenafil). Bayer, West Haven, CT. | ||||
