Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM62UG5)
| Drug Name |
Vemurafenib
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | PLX4032; RG7204; RO5185426; Zelboraf (TN); Vemurafenib (BRAF inhibitor) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
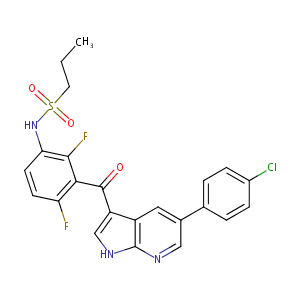 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 489.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Melanoma | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | 2C30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Experimental Cancer Drug Sensitivity Information
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Vemurafenib
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Vemurafenib (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
| DIG |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Formulation |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5893). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Zhang W, Heinzmann D, Grippo JF: Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Vemurafenib. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017 Mar 2. doi: 10.1007/s40262-017-0523-7. | ||||
| 3 | BDDCS predictions, self-correcting aspects of BDDCS assignments, BDDCS assignment corrections, and classification for more than 175 additional drugs | ||||
| 4 | A single-dose mass balance and metabolite-profiling study of vemurafenib in patients with metastatic melanoma. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2015 Mar;3(2):e00113. doi: 10.1002/prp2.113. | ||||
| 5 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | ||||
| 6 | Contribution of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 to the disposition of sorafenib and sorafenib-glucuronide. Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Mar 15;19(6):1458-66. | ||||
| 7 | Differential effects of the oncogenic BRAF inhibitor PLX4032 (vemurafenib) and its progenitor PLX4720 on ABCB1 function. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2014;17(1):154-68. | ||||
| 8 | Vemurafenib for the treatment of melanoma. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2012 Dec;13(17):2533-43. | ||||
| 9 | PLX4032 Mediated Melanoma Associated Antigen Potentiation in Patient Derived Primary Melanoma Cells. J Cancer. 2015 Oct 29;6(12):1320-30. doi: 10.7150/jca.11126. eCollection 2015. | ||||
| 10 | Overcoming melanoma resistance to vemurafenib by targeting CCL2-induced miR-34a, miR-100 and miR-125b. Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 26;7(4):4428-41. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6599. | ||||
| 11 | Melanoma Expressed-CD70 Is Regulated by RhoA and MAPK Pathways without Affecting Vemurafenib Treatment Activity. PLoS One. 2016 Feb 1;11(2):e0148095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148095. eCollection 2016. | ||||
| 12 | Role of the protein kinase BRAF in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016 Aug;20(8):1017-29. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2016.1180367. Epub 2016 May 4. | ||||
| 13 | Paradoxical activation of MEK/ERK signaling induced by B-Raf inhibition enhances DR5 expression and DR5 activation-induced apoptosis in Ras-mutant cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2016 May 25;6:26803. doi: 10.1038/srep26803. | ||||
| 14 | HSP70 Inhibition Limits FAK-Dependent Invasion and Enhances the Response to Melanoma Treatment with BRAF Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2016 May 1;76(9):2720-30. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2137. Epub 2016 Mar 16. | ||||
| 15 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 16 | Product Information. Koselugo (selumetinib). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 17 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Zelboraf (vemurafenib). Genentech, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 19 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 20 | Product Information. Arcapta Neohaler (indacaterol). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Balversa (erdafitinib). Janssen Products, LP, Horsham, PA. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Talzenna (talazoparib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Verzenio (abemaciclib). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 25 | Baciewicz AM "Oral contraceptive drug interactions." Ther Drug Monit 7 (1985): 26-35. [PMID: 2859674] | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Piqray (alpelisib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 27 | Bruderer S, Aanismaa P, Homery MC, et al. "Effect of cyclosporine and rifampin on the pharmacokinetics of macitentan, a tissue-targeting dual endothelin receptor antagonist." AAPS J 14 (2012): 68-78. [PMID: 22189899] | ||||
| 28 | Bengtsson B, Fagerstrom PO "Extrapulmonary effects of terbutaline during prolonged administration." Clin Pharmacol Ther 31 (1982): 726-32. [PMID: 7042176] | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Brintellix (vortioxetine). Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Lincolnshire, IL. | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Aliqopa (copanlisib). Bayer Pharmaceutical Inc, West Haven, CT. | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Tazverik (tazemetostat). Epizyme, Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Myrbetriq (mirabegron). Astellas Pharma US, Inc, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Pifeltro (doravirine). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Tivicay (dolutegravir). ViiV Healthcare, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Orladeyo (berotralstat). BioCryst Pharmaceuticals Inc, Durham, NC. | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Belsomra (suvorexant). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Hetlioz (tasimelteon). Vanda Pharmaceuticals Inc, Rockville, MD. | ||||
| 38 | Product Information. Movantik (naloxegol). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Tabrecta (capmatinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 40 | Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et.al "Successful treatment of l-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors." Leuk Lymphoma 55 (2014): 1670-4. [PMID: 24090500] | ||||
| 41 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 42 | Product Information. Calquence (acalabrutinib). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Imbruvica (ibrutinib). Pharmacyclics Inc, Sunnyvale, CA. | ||||
| 44 | Product Information. Ubrelvy (ubrogepant). Allergan Inc, Irvine, CA. | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Nurtec ODT (rimegepant). Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, New Haven, CT. | ||||
| 46 | Product Information. Reyvow (lasmiditan). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Varubi (rolapitant). Tesaro Inc., Waltham, MA. | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 49 | Product Information. Macrilen (macimorelin). Aeterna Zentaris, Charleston, SC. | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Orgovyx (relugolix). Myovant Sciences, Inc., Brisbane, CA. | ||||
| 51 | Product Information. Nubeqa (darolutamide). Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc., Whippany, NJ. | ||||
| 52 | Product Information. Adempas (riociguat). Bayer Pharmaceutical Inc, West Haven, CT. | ||||
| 53 | Product Information. Odomzo (sonidegib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 54 | Product Information. Diabinese (chlorpropamide). Pfizer US Pharmaceuticals, New York, NY. | ||||
| 55 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 56 | EMA. European Medicines Agency. European Union "EMA - List of medicines under additional monitoring.". | ||||
| 57 | Product Information. Tradjenta (linagliptin). Boehringer Ingelheim, Ridgefield, CT. | ||||
| 58 | Product Information. Orilissa (elagolix). AbbVie US LLC, North Chicago, IL. | ||||
