Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMPC1J7)
| Drug Name |
Clofibrate
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Amotril; Angiokapsul; Anparton; Antilipid; Antilipide; Apolan; Arterioflexin; Arterosol; Artevil; Ateculon; Ateriosan; Athebrate; Atheromide; Atheropront; Athromidin; Atrolen; Atromid; Atromida; Atromidin; Atrovis; Azionyl; Bioscleran; Bresit; CPIB; Cartagyl; Chlorfenisate; Chlorphenisate; Cinnarizin; Citiflus; Claripex; Cloberat; Clobrat; Clofar; Clofibate; Clofibram; Clofibrat; Clofibrato; Clofibratum; Clofinit; Clofipront; Delipid; Deliva; ELPI; EPIB; Fibralem; Gerastop; Hyclorate; Klofibrat; Klofiran; Levatrom; Lipamid; Lipavil; Lipavlon; Lipidsenker; Lipofacton; Lipomid; Liponorm; Liporeduct; Liporil; Liposid; Liprin; Liprinal; Lobetrin; Miscleron; Misclerone; Miskleron; Negalip; Normalip; Normat; Normet; Normolipol; Novofibrate; Persantinat; Recolip; Regardin; Regelan; Robigram; Scrobin; Serofinex; Serotinex; Skerolip; Sklerepmexe; Sklero; Sklerolip; Skleromex; Skleromexe; Ticlobran; Xyduril; Yoclo; Amotril S; Atromid S; Claripex CPIB; Clofibrato [Spanish]; Dura clofibrat; Ethyl chlorophenoxyisobutyrate; Ethyl clofibrate; Regelan N; Vincamin compositum; AY 61123; C 6643; Lipide 500; Oxan 600; AY-61123; Athranid-wirkstoff; Atromid-S; BML2-F02; Chlorophenoxyisobutyrate, Ethyl; Clobren-5F; Clobren-SF; Clofibrate (CLOF); Clofibrato [INN-Spanish]; Clofibratum [INN-Latin]; Clofibric Acid, Ethyl Ester; Ethyl p-chlorophenoxyisobutyrate; Ethyl para-chlorophenoxyisobutyrate; Neo-Atomid; Neo-Atromid; Sklero-Tablinen; Sklero-tablinene; Sklero-tabuls; ATROMID-S (TN); Atromid-S (TN); Atromid-S, Clofibrate; Ethyl alpha-p-chlorophenoxyisobutyrate; Clofibrate (JP15/USP/INN); Clofibrate [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN]; Ethyl 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate; Ethyl 2-(p-chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate; Ethyl alpha-(4-chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate; Ethyl alpha-(p-chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate; Ethyl-alpha-p-chlorophenoxy-isobutyrate
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antilipemic Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
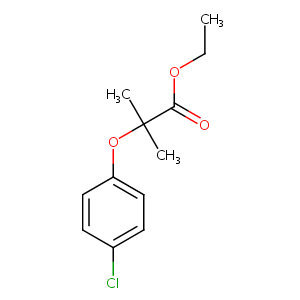 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 242.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 3.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Clofibrate (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
