Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMT81LZ)
| Drug Name |
ARN-509
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | Arn-509 (AR inhibitor) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
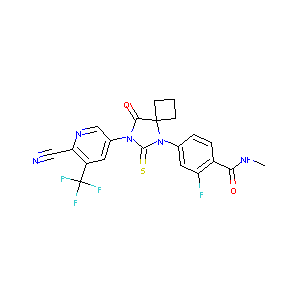 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 477.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| ICD Disease Classification | 02 Neoplasm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease Class | ICD-11: 2C82 Prostate cancer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The Studied Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11:2C82] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as ARN-509
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from ARN-509 (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | 2018 FDA drug approvals.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019 Feb;18(2):85-89. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01946204) A Study of ARN-509 in Men With Non-Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | ||||
| 3 | Apalutamide: first global approval. Drugs. 2018 Apr;78(6):699-705. | ||||
| 4 | Product Information. Tibsovo (ivosidenib). Agios Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 5 | Product Information. Xospata (gilteritinib). Astellas Pharma US, Inc, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 6 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 7 | Product Information. Arcapta Neohaler (indacaterol). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 8 | Product Information. Balversa (erdafitinib). Janssen Products, LP, Horsham, PA. | ||||
| 9 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 10 | Product Information. Verzenio (abemaciclib). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 11 | Product Information. Piqray (alpelisib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 12 | Product Information. Daurismo (glasdegib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 13 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 14 | Product Information. Ingrezza (valbenazine). Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc., San Diego, CA. | ||||
| 15 | Product Information. Aliqopa (copanlisib). Bayer Pharmaceutical Inc, West Haven, CT. | ||||
| 16 | Product Information. Tazverik (tazemetostat). Epizyme, Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 17 | Product Information. Qinlock (ripretinib). Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, Waltham, MA. | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Pifeltro (doravirine). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 19 | Patel S, Robinson R, Burk M "Hypertensive crisis associated with St. John's Wort." Am J Med 112 (2002): 507-8. [PMID: 11959071] | ||||
| 20 | Product Information. Alunbrig (brigatinib). Ariad Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Zepzelca (lurbinectedin). Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Palo Alto, CA. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Lorbrena (lorlatinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Gavreto (pralsetinib). Blueprint Medicines Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Ubrelvy (ubrogepant). Allergan Inc, Irvine, CA. | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Nurtec ODT (rimegepant). Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, New Haven, CT. | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Zeposia (ozanimod). Celgene Corporation, Summit, NJ. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Macrilen (macimorelin). Aeterna Zentaris, Charleston, SC. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Xenleta (lefamulin). Nabriva Therapeutics US, Inc., King of Prussia, PA. | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Nubeqa (darolutamide). Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc., Whippany, NJ. | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Rinvoq (upadacitinib). AbbVie US LLC, North Chicago, IL. | ||||
| 31 | Gunston GD, Mehta U "Potentially serious drug interactions with grapefruit juice." S Afr Med J 90 (2000): 41. [PMID: 10721388] | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Orilissa (elagolix). AbbVie US LLC, North Chicago, IL. | ||||
| 34 | Gelosa P, Castiglioni L, Tenconi M, et.al "Pharmacokinetic drug interactions of the non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants (NOACs)" Pharmacol Res 135 (2018): 60-79. [PMID: 30040996] | ||||
