Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMXLT8C)
| Drug Name |
Sulfisoxazole
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Accuzole; Alphazole; Amidoxal; Astrazolo; Azosulfizin; Bactesulf; Barazae; Chemouag; Cosoxazole; Dorsulfan; ERYZOLE; Entusil; Entusul; Ganda; Gantrisin; Gantrisine; Gantrisona; Gantrosan; Isoxamin; Neazolin; Neoxazoi; Neoxazol; Novazolo; Novosaxazole; Pancid; Renosulfan; Resoxol; Roxosul; Roxoxol; SOXO; Saxosozine; Sodizole; Solfafurazolo; Sosol; Soxamide; Soxazole; Soxisol; Soxitabs; Soxomide; Stansin; Sulbio; Sulfadimethylisoxazole; Sulfafurazol; Sulfafurazole; Sulfafurazolum; Sulfagan; Sulfagen; Sulfaisoxazole; Sulfalar; Sulfapolar; Sulfasol; Sulfasoxazole; Sulfasoxizole; Sulfazin; Sulfisin; Sulfisonazole; Sulfisoxasole; Sulfisoxazol; Sulfisoxazolum; Sulfizin; Sulfizol; Sulfizole; Sulfofurazole; Sulfoxol; Suloxsol; Sulphadimethylisoxazole; Sulphafuraz; Sulphafurazol; Sulphafurazole; Sulphafurazolum; Sulphaisoxazole; Sulphisoxazol; Sulphisoxazole; Sulphofurazole; Sulsoxin; Thiasin; Unisulf; Urisoxin; Uritrisin; Urogan; Vagilia; Azo Gantrisin; Component of Azo Gantrisin; Component of Azo Gantrisin Accuzole; Dorsulfan warthausen; Roxosul tablets; Solfafurazolo [DCIT]; Sulfafuraz ole; Sulfisoxazole [USAN]; Sulfisoxazole dialamine; NU 445; Component of Azo-Sulfizin; G-sox; Gantrisin (TN); J-Sul; Koro-sulf; Norilgan-S; SK-Soxazole; Sulfafurazole (INN); Sulfafurazolum [INN-Latin]; Sulfazin (VAN); Sulfisoxazole-Carc; Tl-azole; US-67; V-Sul; Sulfisoxazole (JP15/USP); U.S.-67; 3,4-Dimethyl-5-sulfanilamidoisoxazole; 3,4-Dimethyl-5-sulfonamidoisoxazole; 3,4-Dimethyl-5-sulphanilamidoisoxazole; 3,4-Dimethyl-5-sulphonamidoisoxazole; 3,4-Dimethylisoxale-5-sulfanilamide; 3,4-Dimethylisoxazole-5-sulfanilamide; 3,4-Dimethylisoxazole-5-sulphanilamide; 3,4-dimethylisoaxazole-5-sulfanilimide; 5-Sulfanilamido-3,4-dimethyl-isoxazole; 5-Sulfanilamido-3,4-dimethylisoxazole; 5-Sulphanilamido-3,4-dimethyl-isoxazole
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinfective Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Enteric bacteria and other eubacteria
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
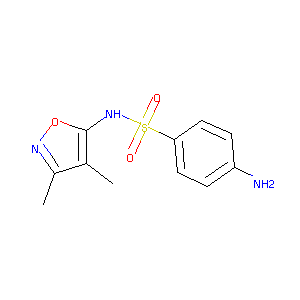 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 267.31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Sulfisoxazole (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
