Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMY4D87)
| Drug Name |
Quazepam
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cetrane; Doral; Dormalin; Oniria; Prosedar; Quazapam; Quazepamum; Quazium; Selepam; Sch 16134; Doral (TN); Dormalin (TN); Quazepamum [INN-Latin]; Sch-161; Sch-16134; Quazepam (JAN/USP); Quazepam [USAN:BAN:INN]; Quazepam (JAN/USP/INN); 7-Chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-2H-1,4-benzodiazepine-2-thione; 7-Chloro-5-(o-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-2H-1,4-benzodiazepine-2-thione; 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-3H-1,4-benzodiazepine-2-thione
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Hypnotics and Sedatives
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
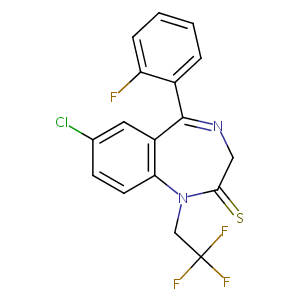 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 386.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Quazepam (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7288). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 3 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 4 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 5 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 6 | Interaction between grapefruit juice and hypnotic drugs: comparison of triazolam and quazepam. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2006 Mar;62(3):209-15. | ||||
| 7 | In vitro metabolism of quazepam in human liver and intestine and assessment of drug interactions. Xenobiotica. 2004 Nov-Dec;34(11-12):1001-11. | ||||
| 8 | US Food and Drug Administration "FDA warns about serious risks and death when combining opioid pain or cough medicines with benzodiazepines requires its strongest warning.". | ||||
| 9 | Amsden GW "Macrolides versus azalides: a drug interaction update." Ann Pharmacother 29 (1995): 906-17. [PMID: 8547740] | ||||
| 10 | Product Information. Isturisa (osilodrostat). Recordati Rare Diseases Inc, Lebanon, NJ. | ||||
| 11 | Product Information. Prevymis (letermovir). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 12 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 13 | Chun AH, Carrigan PJ, Hoffman DJ, Kershner RP, Stuart JD "Effect of antacids on absorption of clorazepate." Clin Pharmacol Ther 22 (1977): 329-35. [PMID: 19188] | ||||
| 14 | Product Information. Xcopri (cenobamate). SK Life Science, Inc., Paramus, NJ. | ||||
| 15 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 16 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 17 | Product Information. Zulresso (brexanolone). Sage Therapeutics, Inc., Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Reyvow (lasmiditan). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 19 | Product Information. Addyi (flibanserin). Sprout Pharmaceuticals, Raleigh, NC. | ||||
| 20 | Product Information. Tasigna (nilotinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Gattex (teduglutide). NPS Pharmaceuticals, Bedminster, NJ. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Fycompa (perampanel). Eisai Inc, Teaneck, NJ. | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Zokinvy (lonafarnib). Eiger BioPharmaceuticals, Palo Alto, CA. | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Prograf (tacrolimus). Fujisawa, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 26 | Doherty MM, Charman WN "The mucosa of the small intestine: how clinically relevant as an organ of drug metabolism?" Clin Pharmacokinet 41 (2002): 235-53. [PMID: 11978143] | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
