Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM0QZBN)
| Drug Name |
Ibandronate
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
BFQ; Acid ibandronico; Ibandronic Acid; Bisphosphonate 2; R484; RPR 102289A; Bondronat (TN); Boniva (TN); Bonviva (TN); Ibandronic acid (INN); Ibandronic acid [INN:BAN]; RPR-102289A; Ibandronic acid, sodium salt, monohydrate; Roche brand of ibandronic acid, sodium salt, monohydrate; [1-hydroxy-3-[methyl(pentyl)amino]-1-phosphonopropyl]phosphonic acid; [1-HYDROXY-3-(METHYL-PENTYL-AMINO)-1-PHOSPHONO-PROPYL]-PHOSPHONIC ACID; (1-Hydroxy-3-(methylpentylamino)propylidene)diphosphonic acid; (1-hydroxy-3-(methylpentylamino)propylidene)bisphosphonate; 1-hydroxy-3-(methylpentylamino)propylidenebisphosphonate
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Bone Density Conservation Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
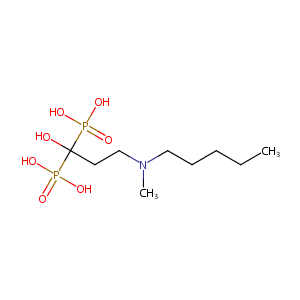 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 1 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 319.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -4.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Ibandronate (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Ibandronate FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 3059). | ||||
| 3 | Reginster JY, Neuprez A, Bruyere O: Ibandronate in profile: drug characteristics and clinical efficacy. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2008 Jul;4(7):941-51. doi: 10.1517/17425255.4.7.941. | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | FDA Approved Drug Products: Boniva Ibandronate Oral Tablets | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 8 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 9 | The bisphosphonate ibandronate promotes apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells in bone metastases. Cancer Res. 2001 Jun 1;61(11):4418-24. | ||||
| 10 | Stimulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by bone-derived transforming growth factor-beta enhances bone metastases in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2006 Feb 15;66(4):2067-73. | ||||
| 11 | Extracellular calcium increases bisphosphonate-induced growth inhibition of breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10(1):R4. doi: 10.1186/bcr1845. Epub 2008 Jan 11. | ||||
| 12 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 13 | Banerjee D, Asif A, Striker L, Preston RA, Bourgoignie JJ, Roth D "Short-term, high-dose pamidronate-induced acute tubular necrosis: The postulated mechanisms of bisphosphonate nephrotoxicity." Am J Kidney Dis 41 (2003): E18. [PMID: 12778436] | ||||
| 14 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 15 | Wong GT, Lee EY, Irwin MG. Contrast induced nephropathy in vascular surgery.?Br J Anaesth. 2016;117 Suppl 2:ii63-ii73. [PMID: 27566809] | ||||
| 16 | Product Information. Zometa (zoledronic acid). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 17 | Product Information. Actonel (risedronate). Procter and Gamble Pharmaceuticals, Cincinnati, OH. | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Bonefos (clodronate). Rhone-Poulenc Rorer Canada Inc, Laval, QC. | ||||
| 19 | Product Information. Exjade (deferasirox). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 20 | Product Information. Prograf (tacrolimus). Fujisawa, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
