Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMRD1QK)
| Drug Name |
Netilmicin
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
NTL; Netilmicina; Netilmicine; Netilmicinum; Netilyn; Netira; Nettacin; Vectacin; NETILMICIN SULFATE; Sch 20569; Netilmicin (INN); Netilmicin [INN:BAN]; Netilmicina [INN-Spanish]; Netilmicine [INN-French]; Netilmicinum [INN-Latin]; Netira (TN); Nettacin (TN); Sch-20569; O-(2,6-Diamino-2,3,4,6-tetradesoxy-alpha-glycero-4-hexenopyranosyl-(1-4)-O-(3-desoxy-4-C-methyl-3-methylamino-beta-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1-6)-2-desoxy-N1-ethyl-D-streptamin; (2R,3R,4R,5R)-2-[(1S,2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-amino-3-[[(2S,3R)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy]-6-(ethylamino)-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol; (2R,3R,4R,5R)-2-[(1S,2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-amino-3-[[3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy]-6-(ethylamino)-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol; (2R,3S,4S,5S)-2-[(1S,2R,3S,4S,6R)-4-amino-3-[[(2S,3R)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy]-6-(ethylamino)-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol; 1-N-Aethylsisomicin; 1-N-Ethylsisomicin; 2-[4-amino-3-[[3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy]-6-(ethylamino)-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol; 4-amino-3-{[3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-6-(ethylamino)-2-hydroxycyclohexyl 3-deoxy-4-c-methyl-3-(methylamino)pentopyranoside
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antibiotics
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Enteric bacteria and other eubacteria
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
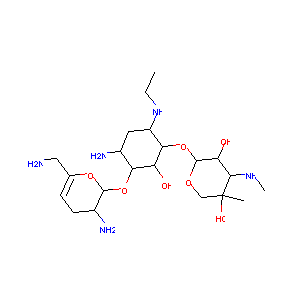 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 3 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 475.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -4.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Netilmicin
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Netilmicin (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
