Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMICA9H)
| Drug Name |
Sulfasalazine
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
sulfasalazine; 599-79-1; Salicylazosulfapyridine; Salazosulfapyridine; Azulfidine; Asulfidine; Salazopyridin; Sulcolon; Azopyrin; Accucol; Colo-Pleon; Salazopiridazin; Salisulf; Reupirin; Benzosulfa; Azopyrine; Salazosulfapyridin; Sulfasalazina; w-t Sasp oral; Sulfasalazinum; Sulfasalazin; Azulfidine EN; Sulfazalazine; Azulfidine EN-tabs; Salazosulfapiridina; Sas-500; Salazosulfapyridinum; Azosulfidin; SASP; Salazo-sulfapyridinum; 5-(p-(2-Pyridylsulfamyl)phenylazo)salicylic acid; SAS-500; Sulfasalizine
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinflammatory Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
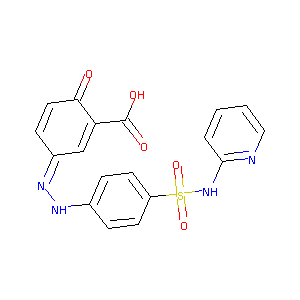 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 398.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -0.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Irritable bowel syndrome | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | DD91.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Sulfasalazine
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Sulfasalazine (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4840). | ||||
| 3 | Sulfasalazine FDA Label | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 8 | The anti-inflammatory mechanism of sulfasalazine is related to adenosine release at inflamed sites. J Immunol. 1996 Mar 1;156(5):1937-41. | ||||
| 9 | Emerging drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2008 Mar;13(1):175-96. | ||||
| 10 | Peptide transporter substrate identification during permeability screening in drug discovery: comparison of transfected MDCK-hPepT1 cells to Caco-2 cells. Arch Pharm Res. 2007 Apr;30(4):507-18. | ||||
| 11 | Small intestinal efflux mediated by MRP2 and BCRP shifts sulfasalazine intestinal permeability from high to low, enabling its colonic targeting. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Aug;297(2):G371-7. | ||||
| 12 | Small-Dosing Clinical Study: Pharmacokinetic, Pharmacogenomic (SLCO2B1 and ABCG2), and Interaction (Atorvastatin and Grapefruit Juice) Profiles of 5 Probes for OATP2B1 and BCRP. J Pharm Sci. 2017 Sep;106(9):2688-2694. | ||||
| 13 | Curcumin inhibits the activity of ABCG2/BCRP1, a multidrug resistance-linked ABC drug transporter in mice. Pharm Res. 2009 Feb;26(2):480-7. | ||||
| 14 | Urinary 6 beta-hydroxycortisol excretion in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1997 Jan;36(1):54-8. | ||||
| 15 | The influence of probiotic treatment on sulfasalazine metabolism in rat. Xenobiotica. 2012 Aug;42(8):791-7. | ||||
| 16 | Developing a metagenomic view of xenobiotic metabolism. Pharmacol Res. 2013 Mar;69(1):21-31. | ||||
| 17 | The role of intestinal bacteria in the metabolism of salicylazosulfapyridine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Jun;181(3):555-62. | ||||
| 18 | Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 2019 Jun;570(7762):462-467. | ||||
| 19 | Down-regulation by nuclear factor kappaB of human 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 2004 Oct;18(10):2440-50. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0441. Epub 2004 Jul 8. | ||||
| 20 | Effect of common medications on the expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry receptors in liver tissue. Arch Toxicol. 2020 Dec;94(12):4037-4041. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02869-1. Epub 2020 Aug 17. | ||||
| 21 | Molecular mechanisms of sulfasalazine-induced T-cell apoptosis. Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Nov;137(5):608-20. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704870. | ||||
| 22 | Adverse effects of sulfasalazine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis are associated with diplotype configuration at the N-acetyltransferase 2 gene. J Rheumatol. 2002 Dec;29(12):2492-9. | ||||
| 23 | Chemotherapeutic drug-induced ABCG2 promoter demethylation as a novel mechanism of acquired multidrug resistance. Neoplasia. 2009 Dec;11(12):1359-70. doi: 10.1593/neo.91314. | ||||
| 24 | Sulfasalazine induces apoptosis of HBx-expressing cells in an NF-kappaB-independent manner. Virus Genes. 2010 Feb;40(1):37-43. doi: 10.1007/s11262-009-0416-4. Epub 2009 Oct 27. | ||||
| 25 | Pharmacogenomic approach reveals a role for the x(c)- cystine/glutamate antiporter in growth and celastrol resistance of glioma cell lines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Mar;332(3):949-58. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.162248. Epub 2009 Dec 9. | ||||
| 26 | Novis BH, Korzets Z, Chen P, Bernheim J "Nephrotic syndrome after treatment with 5-aminosalicylic acid." Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 296 (1988): 1442. [PMID: 3132281] | ||||
| 27 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 28 | Abad S, Moachon L, Blanche P, Bavoux F, Sicard D, Salmon-Ceron D "Possible interaction between glicazide, fluconazole and sulfamethoxazole resulting in severe hypoglycaemia." Br J Clin Pharmacol 52 (2001): 456-7. [PMID: 11678792] | ||||
| 29 | Asplund K, Wiholm BE, Lithner F "Glibenclamide-associated hypoglycaemia: a report on 57 cases." Diabetologia 24 (1983): 412-7. [PMID: 6411511] | ||||
| 30 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 33 | Wong GT, Lee EY, Irwin MG. Contrast induced nephropathy in vascular surgery.?Br J Anaesth. 2016;117 Suppl 2:ii63-ii73. [PMID: 27566809] | ||||
| 34 | Cook DE, Ponte CD "Suspected trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole induced hypoprothrombinemia." J Fam Pract 39 (1994): 589-91. [PMID: 7798864] | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil). Roche Laboratories, Nutley, NJ. | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Rukobia (fostemsavir). ViiV Healthcare, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 38 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Canasa (mesalamine (5-aminosalicylic acid)). Axcan Scandipharm Inc, Birmingham, AL. | ||||
| 41 | Product Information. Tabrecta (capmatinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 42 | Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et.al "Successful treatment of l-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors." Leuk Lymphoma 55 (2014): 1670-4. [PMID: 24090500] | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 44 | Lewis LD, Benin A, Szumlanski CL, et al. "Olsalazine and 6-mercaptopurine-related bone marrow suppression: a possible drug-drug interaction." Clin Pharmacol Ther 62 (1997): 464-75. [PMID: 9357398] | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Nurtec ODT (rimegepant). Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, New Haven, CT. | ||||
| 46 | Product Information. Reyvow (lasmiditan). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Exjade (deferasirox). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Varubi (rolapitant). Tesaro Inc., Waltham, MA. | ||||
| 49 | EMA. European Medicines Agency. European Union "EMA - List of medicines under additional monitoring.". | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Nubeqa (darolutamide). Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc., Whippany, NJ. | ||||
| 51 | Allred AJ, Bowen CJ, Park JW, et al. "Eltrombopag increases plasma rosuvastatin exposure in healthy volunteers." Br J Clin Pharmacol 72 (2011): 321-9. [PMID: 21434975] | ||||
| 52 | Product Information. Prograf (tacrolimus). Fujisawa, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
