Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMMUCG4)
| Drug Name |
Eicosapentaenoic acid/docosa-hexaenoic acid
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Docosahexaenoic acid; Doconexent; Cervonic acid; 6217-54-5; all-cis-DHA; Doconexentum; Doconexento; Doxonexent; (4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic acid; AquaGrow Advantage; all-Z-Docosahexaenoic acid; Martek DHA HM; Ropufa 60; cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-Docosahexaenoic acid; Docosahexaenoate; UNII-ZAD9OKH9JC; (4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-Docosahexaenoic acid; Docosahexaenoic acid (all-Z); CCRIS 7670; all-cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-Docosahexaenoic acid; ZAD9OKH9JC; all-cis-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic acid; CHEMBL367149; Espanova (TN); DOCOSAHEXAENOIC ACID
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
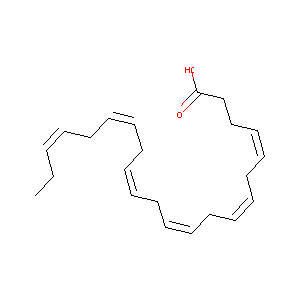 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 2 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 328.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 6.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Hypertriglyceridemia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | 5C80.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
