Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMGFWSM)
| Drug Name |
Zaleplon
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Sonata; Zalaplon; Zerene; CL 284846; L 846; L846; LJC 10846; ZAL 846; AZ-007; CL 284,846; CL-284846; CL284,846; L-846; LJC-10846; SKP-1041; Sonata (TN); Staccato-zaleplon; Starnoc (TN); ZAL-846; Zaleplon [USAN:INN]; Zaleplon (JAN/USAN/INN); N-[3-(3-cyanopyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-yl)phenyl]-N-ethylacetamide; N-(3-(3-Cyanopyrazolo(1,5-a)pyrimidin-7-yl)phenyl)-N-ethylacetamide; 3'-(3-Cyanopyrazolo(1,5-a)pyrimidin-7-yl)-N-ethylacetanilide; 3'-(3-Cyanopyrazolo(1,5-alpha)pyrimidin-7-yl)-N-ethylacetanilide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Hypnotics and Sedatives
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
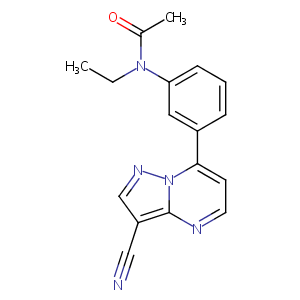 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 305.33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Zaleplon (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4345). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Zaleplon FDA Label | ||||
| 3 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 4 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 5 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 6 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 7 | Metabolism of zaleplon by human liver: evidence for involvement of aldehyde oxidase. Xenobiotica. 2002 Oct;32(10):835-47. | ||||
| 8 | Drug Interactions Flockhart Table | ||||
| 9 | Characterization of aldehyde oxidase enzyme activity in cryopreserved human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2012 Feb;40(2):267-75. | ||||
| 10 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 11 | US Food and Drug Administration "FDA warns about serious risks and death when combining opioid pain or cough medicines with benzodiazepines requires its strongest warning.". | ||||
| 12 | Product Information. Ketek (telithromycin). Aventis Pharmaceuticals, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 13 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 14 | Product Information. Tukysa (tucatinib). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 15 | US Food and Drug Administration "FDA warns about serious risks and death when combining opioid pain or cough medicines with benzodiazepines requires its strongest warning.". | ||||
| 16 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 17 | Product Information. Xcopri (cenobamate). SK Life Science, Inc., Paramus, NJ. | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Sonata (zaleplon) Wyeth-Ayerst Laboratories, Philadelphia, PA. | ||||
| 19 | Auclair B, Berning SE, Huitt GA, Peloquin CP "Potential interaction between itraconazole and clarithromycin." Pharmacotherapy 19 (1999): 1439-44. [PMID: 10600094] | ||||
| 20 | Product Information. Fortovase (saquinavir) Roche Laboratories, Nutley, NJ. | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Orladeyo (berotralstat). BioCryst Pharmaceuticals Inc, Durham, NC. | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Lorbrena (lorlatinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Zulresso (brexanolone). Sage Therapeutics, Inc., Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Reyvow (lasmiditan). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Addyi (flibanserin). Sprout Pharmaceuticals, Raleigh, NC. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Thalomid (thalidomide). Celgene Corporation, Warren, NJ. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Tasigna (nilotinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Alphagan (brimonidine ophthalmic). Allergan Inc, Irvine, CA. | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Fycompa (perampanel). Eisai Inc, Teaneck, NJ. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Zokinvy (lonafarnib). Eiger BioPharmaceuticals, Palo Alto, CA. | ||||
| 33 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Prograf (tacrolimus). Fujisawa, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
