Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMHAQCO)
| Drug Name |
Trichlormethiazide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Achletin; Anistadin; Aponorin; Aquazide; Carvacron; Chlopolidine; Cretonin; Diurazida; Diurese; Diuroral;Esmarin; Eurinol; Fluitran; Flurese; Flutra; Gangesol; Hydrotrichlorothiazide; Intromene; Isestran; Kubacron; Metahydrin; Metatensin; Nakva; Naqua; Naquasone; Schebitran; Tachionin; Tolcasone; Trichlordiuride; Trichlorex; Trichlormas; Trichlormetazid; Trichlormethiazid; Trichlormethiazidum; Trichloromethiadiazide; Trichloromethiazide; Triclordiuride; Triclormetiazida; Triclormetiazide; Triflumen;American Urologicals Brand of Trichloromethiazide; Jones Brand of Trichloromethiazide; Schering Brand of Trichlormethiazide; Triclormetiazide [DCIT]; Triclormetiazide [Italian]; Achletin (TN); Ciba 7057-Su; Diu-Hydrin; Flurese (VAN); Naqua (TN); Salurin (wadel); Trichlormethiazide W/ Reserpine; Trichlormethiazide [INN:JAN]; Trichlormethiazidum [INN-Latin]; Trichloromethiazide, 6; Triclormetiazida[INN-Spanish]; Triflumen (TN); Diu-Hydrin (TN); Trichlormethiazide (JP15/USP/INN); (+-)-6-Chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide; 2H-1,2,4-Benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-, 1,1-dioxide; 2H-1,2,4-Benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-,1,1-dioxide; 3-(Dichloromethyl)-6-chloro-7-sulfamoyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide; 3-(Dichloromethyl)-6-chloro-7-sulfamoyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide; 3-Dichloromethyl-6-chloro-7-sulfamoyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide; 3-Dichloromethyl-6-chloro-7-sulfamyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide; 3-Dichloromethyl-6-chloro-7-sulfamyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine1,1-dioxide; 3-Dichloromethylhydrochlorothiazide; 6-Chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide; 6-Chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide1,1-dioxide; 6-Chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)3,4-dihydro-7-sulfamoyl-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide; 6-Chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)3,4-dihydro-7-sulfamyl-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide; 6-Chloro-3-[dichloromethyl]-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide-1,1-dioxide; 6-Chloro-3-dichloromethyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-Dioxide; 6-Chloro-3-dichloromethyl-7-sulfamyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine1,1-dioxide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antihypertensive Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
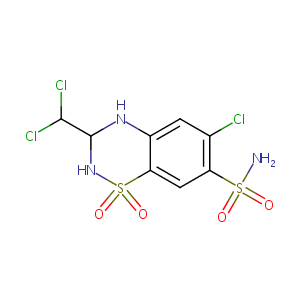 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 380.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 0.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Trichlormethiazide
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Trichlormethiazide (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
