Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMT5HA4)
| Drug Name |
Ketamine
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Calypsol; Cetamina; Green; Ketaject; Ketalar; Ketaminum; Ketanest; Ketoject; Ketolar; Tekam; KETAMINE HCL; Ketalar base; Ketamine Base; Special K; Special K [street name]; CLSTA 20; T385; Cetamina [INN-Spanish]; Dl-Ketamine; Ketalar (TN); Ketamine (INN); Ketamine [INN:BAN]; Ketaminum [INN-Latin]; Ketanest (TN); Ketaset (TN); Tekam (TN); Cyclohexanone, 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)-(9CI); Cyclohexanone, 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)-, (+-)-(9CI); Cyclohexanone, 2-(o-chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)-, (+/-)-(8CI); (+/-)-2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexanone; (+/-)-2-(o-Chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexanone; 2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexanone; 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexan-1-one; 2-(Methylamino)-2-(2-chlorophenyl)cyclohexanone; 2-(o-Chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)-cyclohexanone; 2-(o-Chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexanone
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Analgesics
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
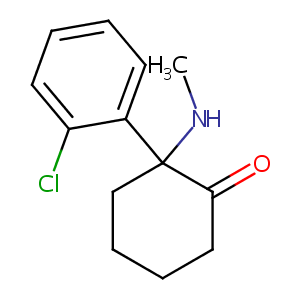 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 237.72 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 2.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Ketamine (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
