Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM7PQIK)
| Drug Name |
Nitrofurantoin
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Alfuran; Benkfuran; Berkfuran; Berkfurin; Ceduran; Chemiofuran; Cistofuran; Cyantin; Cystit; Dantafur; Furabid; Furachel; Furadantin; Furadantine; Furadantoin; Furadoine; Furadonin; Furadonine; Furadoninum; Furadontin; Furalan; Furaloid; Furantoin; Furatoin; Furedan; Furina; Furobactina; Furodantin; Furophen; Gerofuran; Ituran; Macpac; Macrobid; Macrodantin; Macrodantina; Macrofuran; Macrofurin; NITROFURANTION; Nierofu; Nifurantin; Nifuretten; Nitoin; Nitrex; Nitrofuradantin; Nitrofurantoina; Nitrofurantoine; Nitrofurantoinum; Novofuran; Orafuran; Parfuran; Phenurin; PiyEloseptyl; Siraliden; Trantoin; Uerineks; Urantoin; Urizept; Urodil; Urodin; Urofuran; Urofurin; Urolisa; Urolong; Welfurin; Zoofurin; Fua Med; Furadantin Retard; Furadantina MC; Furadantine mc; Furophen T; NITROFURANTOIN MACROCRYSTALLINE; Nitrofurantoina [DCIT]; Fua-med; Fur-ren; Furadantin (TN); Furadantine-MC; Macrobid (TN); Macrodantin (TN); N-Toin; ND-3320; ND-7248; NITROFURANTOIN, MACROCRYSTALLINE; Nitro Macro (TN); Nitrofur-C; Nitrofurantoine [INN-French]; Nitrofurantoinum [INN-Latin]; Ro-Antoin; Urantoin (TN); Uro-Selz; Uro-Tablinen; Uro-tablineu; Usaf ea-2; Nitrofurantoin (JAN/USP/INN); Nitrofurantoin [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN]; N-(5-Nitrofurfurylidene)-1-aminohydantoin; N-(5-Nitro-2-furfurylidene)-1-aminohydantoin; N-(5-Nitro-2-furfurylideno)-1-aminohydantoina; N-(5-Nitro-2-furfurylideno)-1-aminohydantoina [Polish]; N-(5-nitro-2-furfurylidene)-1-aminohyda ntoin; 1-(((5-nitro-2-furanyl)methylene)amino)-2,4-imidazolidinedione; 1-((5-Nitrofurfurylidene)amino)hydantoin; 1-(5-Nitro-2-furfurylidenamino)hydantoin; 1-(5-Nitro-2-furfurylideneamino)hydantoin; 1-[(5-:nitrofurfurylidene)amino]hydantoin; 1-[(5-Nitrofurfurylidene)amino]hydantoin; 1-[(E)-(5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methylideneamino]imidazolidine-2,4-dione; 1-[[(5-Nitro-2-furanyl)methylene]amino]-2,4-imidazolidinedione; 1-{[(1E)-(5-nitro-2-furyl)methylene]amino}imidazolidine-2,4-dione; 1-{[(1E)-(5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methylidene]amino}imidazolidine-2,4-dione; 5-Nitrofurantoin
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinfective Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Gram negative and gram positive bacteria
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
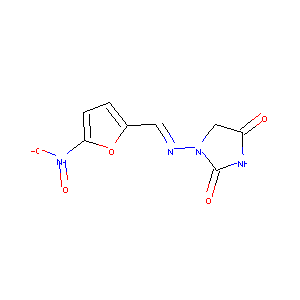 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 238.16 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -0.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Nitrofurantoin (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (NDA) 009175. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Pharmacological properties of oral antibiotics for the treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infections. J Chemother. 2017 Dec;29(sup1):10-18. doi: 10.1080/1120009X.2017.1380357. | ||||
| 3 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 4 | Critical Evaluation of Human Oral Bioavailability for Pharmaceutical Drugs by Using Various Cheminformatics Approaches | ||||
| 5 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 6 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 7 | Niazi S, Vishnupad KS, Veng-Pedersen P: Absorption and disposition characteristics of nitrofurantoin in dogs. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1983 Jul-Sep;4(3):213-23. | ||||
| 8 | On the nature of the adaptive response induced by mitomycin C in Vibrio cholerae OGAWA 154 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996 Mar 27;220(3):509-14. | ||||
| 9 | The breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) affects pharmacokinetics, hepatobiliary excretion, and milk secretion of the antibiotic nitrofurantoin. Mol Pharmacol. 2005 May;67(5):1758-64. | ||||
| 10 | Role of cytochrome P450 reductase in nitrofurantoin-induced redox cycling and cytotoxicity. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008 Mar 15;44(6):1169-79. | ||||
| 11 | Reduction of polynitroaromatic compounds: the bacterial nitroreductases. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008 May;32(3):474-500. | ||||
| 12 | The human gut microbiota: metabolism and perspective in obesity. Gut Microbes. 2018 Jul 4;9(4):308-325. | ||||
| 13 | Conversion of NfsA, the major Escherichia coli nitroreductase, to a flavin reductase with an activity similar to that of Frp, a flavin reductase in Vibrio harveyi, by a single amino acid substitution. J Bacteriol. 1998 Jan;180(2):422-5. | ||||
| 14 | Bacillus subtilis isolated from the human gastrointestinal tract. Res Microbiol. 2009 Mar;160(2):134-43. | ||||
| 15 | Mechanism of metronidazole-resistance by isolates of nitroreductase-producing Enterococcus gallinarum and Enterococcus casseliflavus from the human intestinal tract. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2003 Aug 29;225(2):195-200. | ||||
| 16 | Isolation of nitrofurantoin-resistant mutants of nitroreductase-producing Clostridium sp. strains from the human intestinal tract. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998 May;42(5):1121-6. | ||||
| 17 | Biotransformation of 1-nitropyrene in intestinal anaerobic bacteria. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(11):993-1005. | ||||
| 18 | Early identification of clinically relevant drug interactions with the human bile salt export pump (BSEP/ABCB11). Toxicol Sci. 2013 Dec;136(2):328-43. | ||||
| 19 | Effects of the flavonoid chrysin on nitrofurantoin pharmacokinetics in rats: potential involvement of ABCG2. Drug Metab Dispos. 2007 Feb;35(2):268-74. | ||||
| 20 | Stimulation of de novo glutathione synthesis by nitrofurantoin for enhanced resilience of hepatocytes. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2022 Oct;38(5):847-864. doi: 10.1007/s10565-021-09610-3. Epub 2021 May 22. | ||||
| 21 | A Gene Expression Biomarker Predicts Heat Shock Factor 1 Activation in a Gene Expression Compendium. Chem Res Toxicol. 2021 Jul 19;34(7):1721-1737. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.0c00510. Epub 2021 Jun 25. | ||||
| 22 | Roles of DT diaphorase in the genotoxicity of nitroaromatic compounds in human and fish cell lines. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1997 Oct 10;52(2):137-48. doi: 10.1080/00984109708984057. | ||||
| 23 | Evaluating the Role of Multidrug Resistance Protein 3 (MDR3) Inhibition in Predicting Drug-Induced Liver Injury Using 125 Pharmaceuticals. Chem Res Toxicol. 2017 May 15;30(5):1219-1229. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.7b00048. Epub 2017 May 4. | ||||
| 24 | Effect of common medications on the expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry receptors in liver tissue. Arch Toxicol. 2020 Dec;94(12):4037-4041. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02869-1. Epub 2020 Aug 17. | ||||
| 25 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 26 | Jaffe JM "Effect of propantheline on nitrofurantoin absorption." J Pharm Sci 64 (1975): 1729-30. [PMID: 1185550] | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 29 | Heipertz R, Pilz H "Interaction of nitrofurantoin with diphenylhydantoin." J Neurol 218 (1978): 297-301. [PMID: 81279] | ||||
| 30 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Accolate (zafirlukast). Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 33 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 35 | Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et.al "Successful treatment of l-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors." Leuk Lymphoma 55 (2014): 1670-4. [PMID: 24090500] | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 37 | Argov Z, Mastaglia FL "Drug-induced peripheral neuropathies." Br Med J 1 (1979): 663-6. [PMID: 219931] | ||||
| 38 | Agencia Espaola de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios Healthcare "Centro de informacion online de medicamentos de la AEMPS - CIMA.". | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. ReVia (naltrexone). DuPont Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
