Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM15HL8)
| Drug Name |
Clindamycin
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Antirobe; CLDM; CLY; Chlolincocin; Chlorlincocin; Chlorodeoxylincomycin; Chlorolincomycin; Cleocin; ClindaDerm; Clindamicina; Clindamycine; Clindamycinum; Clinimycin; Dalacine; Klimicin; Sobelin; Zindaclin; Cleocin HCl; Cleocin T Gel; Cleocin T Lotion; Cleocin T Topical Solution; Clindamycine [French]; Dalacin C; Dalacin C Flavored Granules; Dalacin C Phosphate; Dalacin T Topical Solution; ResiDerm A; Klindan 300; U 21251; Cleocin (TN); Clindacin (TN); Clindamicina [INN-Spanish]; Clindamycin & Interleukin 12; Clindamycin & VRC3375; Clindamycine [INN-French]; Clindamycinum [INN-Latin]; Dalacin (TN); Evoclin (TN); U-21251; CLINDA & IL-12; Clindamycin (USAN/INN); Clindamycin [USAN:BAN:INN]; U-21,251; 7(S)-Chloro-7-deoxylincomycin; 7-CDL; 7-Chloro-7-deoxylincomycin; 7-Chlorolincomycin; 7-Deoxy-7(S)-chlorolincomycin
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antibiotics
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Staphylococcus aureusStreptococcus pneumoniaeStreptococcus pyogenesClostridium perfringensFusobacterium nucleatumStaphylococcus epidermidisStreptococcus agalactiaeStreptococcus anginosusStreptococcus mitisStreptococcus oralisFinegoldia magnaPropionibacterium acnesFusobacterium necrophorumPeptostreptococcus anaerobiusPrevotella melaninogenicaActinomyces israeliiClostridium clostridioformeEggerthella lentaParvimonas micraPrevotella biviaPrevotella intermedia
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
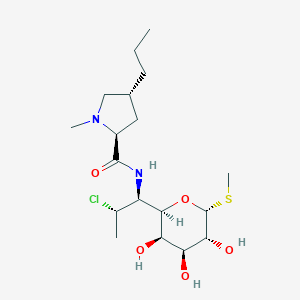 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 425 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 2.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Clindamycin (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Clindamycin FDA Label | ||||
| 3 | FDA Approved Drug Products: Cleocin (clindamycin hydrochloride) oral capsules | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Leigh DA: Antibacterial activity and pharmacokinetics of clindamycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jun;7 Suppl A:3-9. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.suppl_a.3. | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 8 | Bouazza N, Pestre V, Jullien V, Curis E, Urien S, Salmon D, Treluyer JM: Population pharmacokinetics of clindamycin orally and intravenously administered in patients with osteomyelitis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;74(6):971-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04292.x. | ||||
| 9 | Structural basis for the interaction of antibiotics with the peptidyl transferase centre in eubacteria. Nature. 2001 Oct 25;413(6858):814-21. | ||||
| 10 | In vitro metabolism of clindamycin in human liver and intestinal microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2003 Jul;31(7):878-87. | ||||
| 11 | Comparison of antimicrobial susceptibility, beta-lactamase production, plasmid analysis and serum bactericidal activity in Edwardsiella tarda, E. ictaluri and E. hoshinae. J Med Microbiol. 1993 Oct;39(4):273-81. | ||||
| 12 | Chloramphenicol causes mitochondrial stress, decreases ATP biosynthesis, induces matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression, and solid-tumor cell invasion. Toxicol Sci. 2010 Jul;116(1):140-50. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq085. Epub 2010 Mar 25. | ||||
| 13 | A comprehensive in vitro and in silico analysis of antibiotics that activate pregnane X receptor and induce CYP3A4 in liver and intestine. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008 Aug;36(8):1689-97. | ||||
| 14 | Systems pharmacological analysis of drugs inducing stevens-johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Chem Res Toxicol. 2015 May 18;28(5):927-34. doi: 10.1021/tx5005248. Epub 2015 Apr 3. | ||||
| 15 | Bernard A, Kermarrec G, Parize P, et.al "Dramatic reduction of clindamycin serum concentration in staphylococcal osteoarticular infection patients treated with the oral clindamycin-rifampicin combination." J Infect 71 (2015): 200-6. [PMID: 25936632] | ||||
| 16 | Product Information. Cleocin (clindamycin). Pharmacia and Upjohn, Kalamazoo, MI. | ||||
| 17 | Brause BD, Romankiewicz JA, Gotz V, Franklin JE Jr, Roberts RB "Comparative study of diarrhea associated with clindamycin and ampicillin therapy." Am J Gastroenterol 73 (1980): 244-8. [PMID: 7405925] | ||||
| 18 | Alahdal O, Bevan DR "Clindamycin-induced neuromuscular blockade." Can J Anaesth 42 (1995): 614-7. [PMID: 7553999] | ||||
| 19 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 20 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
