Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMUYNEI)
| Drug Name |
Amoxicillin
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
AMPC; Actimoxi; Amoclen; Amolin; Amopen; Amopenixin; Amoxi; Amoxibiotic; Amoxicaps; Amoxicilina; Amoxicillanyl; Amoxicilline; Amoxicillinum; Amoxiden; Amoxil; Amoxivet; Amoxycillin; Anemolin; Aspenil; Biomox; Bristamox; Cemoxin; Clamoxyl; Delacillin; DisperMox; Efpenix; Flemoxin; Hiconcil; Histocillin; Hydroxyampicillin; Ibiamox; Imacillin; Lamoxy; Larotid; Moxacin; Moxal; Moxatag; Ospamox; Pamoxicillin; Piramox; Polymox; Robamox; Sumox; Tolodina; Trimox; Unicillin; Utimox; Vetramox; Wymox; AMOXICILLIN CRYSTALLINE; AMOXICILLIN PEDIATRIC; Amoxicillin anhydrous; Amoxicilline [INN]; Amoxycillin Trihydrate; Metafarma capsules; Metifarma capsules; Sawamox PM; BLP 1410; AMK (TN); Actimoxi (TN); Alphamox (TN); Amoksibos (TN); Amoksiklav (TN); Amoxi-Mast; Amoxibiotic (TN); Amoxicilina (TN); Amoxicilina [INN-Spanish]; Amoxicillin (INN); Amoxicillin (TN); Amoxicillin (anhydrous); Amoxicilline [INN-French]; Amoxicillinum [INN-Latin]; Amoxiclav (TN); Amoxidal (TN); Amoxil (TN); Amoxin (TN); Apo-Amoxi; Augmentin (TN); BL-P 1410; BRL-2333; Bactox (TN); Betalaktam (TN); Cilamox (TN); Clamoxyl (TN); Curam (TN); D-Amoxicillin; Dedoxil (TN); Dispermox (TN); Duomox (TN); Enhancin (TN); Geramox (TN); Gimalxina (TN); Hiconcil (TN); Isimoxin (TN); Klavox (TN); Lamoxy (TN); Moxatag (TN); Moxilen (TN); Moxypen (TN); Moxyvit (TN); Nobactam (TN); Novamoxin (TN); Ospamox (TN); P-Hydroxyampicillin; Pamoxicillin (TN); Panamox (TN); Panklav (TN); Polymox (TN); Ro 10-8756; Samthongcillin (TN); Sandoz (TN); Senox (TN); Sinacilin (TN); Tolodina (TN); Trimox (TN); Wymox (TN); Yucla (TN); Zerrsox (TN); Zimox (TN); Apo-Amoxi (TN); Alpha-Amino-p-hydroxybenzylpenicillin; D-2-Amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamidopenicillanic acid; D-(-)-alpha-Amino-p-hydroxybenzylpenicillin; (-)-6-(2-Amino-2-(P-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo-(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid; (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; (2S,5R,6R)-6-{[(2R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetyl]amino}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; 4-Thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 6-(2-amino-2-(p-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, D-(8CI); 6-(D-(-)-alpha-Amino-p-hydroxyphenylacetamido)penicillanic acid; 6-(D-(-)-p-Hydroxy-alpha-aminobenzyl)penicillin; 6-(p-Hydroxy-alpha-aminophenylacetamido)penicillanic acid; 6beta-[(2R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-2,2-dimethylpenam-3alpha-carbonyl; 6beta-[(2R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-2,2-dimethylpenam-3alpha-carboxylic acid
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antibiotics
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Enteric bacteria and other eubacteriaGram negative and gram positive bacteriaStreptococcus pyogenesStreptococcus pneumoniaeSalmonella typhiBorrelia burgdorferiChlamydia psittaciChlamydia pneumoniae
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
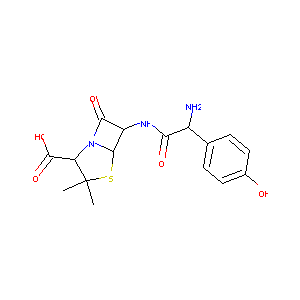 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 365.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Amoxicillin (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Amoxicillin FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Emerging therapies for the treatment and prevention of otitis media. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2006 May;11(2):251-64. | ||||
| 3 | Comparative clinical pharmacology of amoxicillin and ampicillin administered orally. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jun;1(6):504-7. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.6.504. | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | de Velde F, de Winter BC, Koch BC, van Gelder T, Mouton JW: Non-linear absorption pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin: consequences for dosing regimens and clinical breakpoints. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016 Oct;71(10):2909-17. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkw226. Epub 2016 Jun 20. | ||||
| 6 | Bodey GP, Nance J: Amoxicillin: in vitro and pharmacological studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):358-62. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.358. | ||||
| 7 | Bauman JN, Frederick KS, Sawant A, Walsky RL, Cox LM, Obach RS, Kalgutkar AS: Comparison of the bioactivation potential of the antidepressant and hepatotoxin nefazodone with aripiprazole, a structural analog and marketed drug. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008 Jun;36(6):1016-29. doi: 10.1124/dmd.108.020545. Epub 2008 Mar 10. | ||||
| 8 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 9 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 10 | HLA alleles influence the clinical signature of amoxicillin-clavulanate hepatotoxicity. PLoS One. 2013 Jul 9;8(7):e68111. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068111. Print 2013. | ||||
| 11 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 12 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 13 | Interactions of amoxicillin and cefaclor with human renal organic anion and peptide transporters. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 Apr;34(4):547-55. | ||||
| 14 | The anti-influenza drug oseltamivir exhibits low potential to induce pharmacokinetic drug interactions via renal secretion-correlation of in vivo and in vitro studies. Drug Metab Dispos. 2002 Jan;30(1):13-9. | ||||
| 15 | Human intestinal transporter database: QSAR modeling and virtual profiling of drug uptake, efflux and interactions. Pharm Res. 2013 Apr;30(4):996-1007. | ||||
| 16 | High-dose rabeprazole/amoxicillin therapy as the second-line regimen after failure to eradicate H. pylori by triple therapy with the usual doses of a proton pump inhibitor, clarithromycin and amoxicillin. Hepatogastroenterology. 2003 Nov-Dec;50(54):2274-8. | ||||
| 17 | Interspecies dissemination of a mobilizable plasmid harboring blaIMP-19 and the possibility of horizontal gene transfer in a single patient. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Aug 22;60(9):5412-9. | ||||
| 18 | Genomic characterization of an extensively-drug resistance Salmonella enterica serotype Indiana strain harboring bla NDM-1 gene isolated from a chicken carcass in China. Microbiol Res. 2017 Nov;204:48-54. | ||||
| 19 | Detection and characterization of beta-lactamase genes in subgingival bacteria from patients with refractory periodontitis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005 Jan 15;242(2):319-24. | ||||
| 20 | Antimicrobial drugs used in the management of anaerobic infections in children. Drugs. 1983 Dec;26(6):520-9. | ||||
| 21 | IncU plasmid harbouring bla CTX-M-8 in multidrug-resistant Shigella sonnei in Brazil. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2018 Sep;14:99-100. | ||||
| 22 | A novel quorum-quenching N-acylhomoserine lactone acylase from Acidovorax sp. strain MR-S7 mediates antibiotic resistance. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Jun 16;83(13). pii: e00080-17. | ||||
| 23 | Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance genes in Bacteroides spp. and Prevotella spp. Dutch clinical isolates. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019 Sep;25(9):1156.e9-1156.e13. | ||||
| 24 | Major phenylpropanoid-derived metabolites in the human gut can arise from microbial fermentation of protein. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013 Mar;57(3):523-35. | ||||
| 25 | The prevalence of beta-lactamase producing bacteria in subgingival plaque and their sensitivity to Augmentin. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1990 Jun;28(3):180-4. | ||||
| 26 | ACI-1 beta-lactamase is widespread across human gut microbiomes in Negativicutes due to transposons harboured by tailed prophages. Environ Microbiol. 2018 Jun;20(6):2288-2300. | ||||
| 27 | Beta-lactamase production and susceptibilities to amoxicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, ticarcillin, ticarcillin-clavulanate, cefoxitin, imipenem, and metronidazole of 320 non-Bacteroides fragilis Bacteroides isolates and 129 fusobacteria from 28 U.S. centers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Aug;34(8):1546-50. | ||||
| 28 | Effect of CO2 on susceptibilities of anaerobes to erythromycin, azithromycin, clarithromycin, and roxithromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Feb;38(2):211-6. | ||||
| 29 | ACI-1 from Acidaminococcus fermentans: characterization of the first beta-lactamase in Anaerobic cocci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000 Nov;44(11):3144-9. | ||||
| 30 | Presence of the cfxA gene in Bacteroides distasonis. Res Microbiol. 2003 Jun;154(5):369-74. | ||||
| 31 | Beta-lactamase production, beta-lactam sensitivity and resistance to synergy with clavulanate of 737 Bacteroides fragilis group organisms from thirty-three US centres. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Sep;26(3):361-70. | ||||
| 32 | Prevotella strains and lactamic resistance gene distribution in different oral environments of children with pulp necrosis. Int Endod J. 2018 Nov;51(11):1196-1204. | ||||
| 33 | High prevalence of beta-lactam and macrolide resistance genes in human oral Capnocytophaga species. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014 Feb;69(2):381-4. | ||||
| 34 | Yersinia enterocolitica and Photorhabdus asymbiotica beta-lactamases BlaA are exported by the twin-arginine translocation pathway. Int J Med Microbiol. 2013 Jan;303(1):16-24. | ||||
| 35 | Xenorhabdus luminescens (DNA hybridization group 5) from human clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1594-600. Case Reports | ||||
| 36 | High prevalence of cfxA beta-lactamase in aminopenicillin-resistant Prevotella strains isolated from periodontal pockets. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2002 Apr;17(2):85-8. | ||||
| 37 | Characterization of drug-specific signaling between primary human hepatocytes and immune cells. Toxicol Sci. 2017 Jul 1;158(1):76-89. | ||||
| 38 | Modulation of steroidogenic gene expression and hormone production of H295R cells by pharmaceuticals and other environmentally active compounds. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007 Dec 1;225(2):142-53. | ||||
| 39 | Systemic drugs inducing non-immediate cutaneous adverse reactions and contact sensitizers evoke similar responses in THP-1 cells. J Appl Toxicol. 2015 Apr;35(4):398-406. doi: 10.1002/jat.3033. Epub 2014 Aug 4. | ||||
| 40 | Effect of penicillin-based antibiotics, amoxicillin, ampicillin, and piperacillin, on drug-metabolizing activities of human hepatic cytochromes P450. J Toxicol Sci. 2016 Feb;41(1):143-6. | ||||
| 41 | Systems pharmacological analysis of drugs inducing stevens-johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Chem Res Toxicol. 2015 May 18;28(5):927-34. doi: 10.1021/tx5005248. Epub 2015 Apr 3. | ||||
| 42 | Alexander DP, Russo ME, Fohrman DE, Rothstein G "Nafcillin-induced platelet dysfunction and bleeding." Antimicrob Agents Chemother 23 (1983): 59-62. [PMID: 6830209] | ||||
