Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMIXC7G)
| Drug Name |
Zoledronate
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Aclasta; Reclast; ZOL; Zometa; Novartis brand of zoledronic acid; Zoledronic acid; Zometa Concentrate; Bisphosphonate 3; CGP 42446; CGP 42446A; Aclasta (TN); CGP 42'446; CGP-42446; KS-1132; Reclast (TN); Zoledronic acid (INN); Zoledronic acid [USAN:INN]; Zomera (TN); Zometa (Novartis); Zometa (TN); CGP-42'446; Zometa, Zomera, Aclasta and Reclast, Zoledronic Acid; [1-hydroxy-2-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethane-1,1-diyl]bis(phosphonic acid); (1-Hydroxy-2-imidazol-1-ylethylidene)diphosphonic acid; (1-hydroxy-2-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethylidene)bisphosphonic acid; (1-hydroxy-2-imidazol-1-yl-1-phosphonoethyl)phosphonic acid; (1-hydroxy-2-imidazol-1-yl-phosphonoethyl)phosphonic acid monohydrate; 2-(imidazol-1-yl)-1-hydroxyethane-1,1-diphosphonic acid; 2-(imidazol-1-yl)-1-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-bisphosphonic acid
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Bone Density Conservation Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
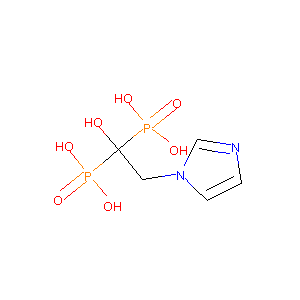 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 1 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 272.09 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -4.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Experimental Cancer Drug Sensitivity Information
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Zoledronate
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Zoledronate (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
| 1 | In vitro cytotoxicity of zoledronate (nitrogen-containing bisphosphonate: NBP) and/or etidronate (non-NBP) in tumour cells and periodontal cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2013 Jun;58(6):628-37. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Giant Cell Tumor of Bone: Review of Current Literature, Evaluation, and Treatment Options. J Knee Surg. 2019 Apr;32(4):331-336. | ||||
| 3 | Paget's Disease of Bone: Diagnosis and Treatment. Am J Med. 2018 Nov;131(11):1298-1303. | ||||
| 4 | Current and future treatments of bone metastases. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2008 Dec;13(4):609-27. | ||||
| 5 | Clinical, radiographic, and biochemical characterization of multiple myeloma patients with osteonecrosis of the jaw. Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Apr 15;14(8):2387-95. | ||||
| 6 | AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS/AMERICAN COLLEGE OF ENDOCRINOLOGY CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF POSTMENOPAUSAL OSTEOPOROSIS-2020 UPDATE. Endocr Pract. 2020 May;26(Suppl 1):1-46. | ||||
| 7 | Shiraki M, Tanaka S, Suzuki H, Ueda S, Nakamura T: Safety, pharmacokinetics, and changes in bone metabolism associated with zoledronic acid treatment in Japanese patients with primary osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2017 Nov;35(6):675-684. doi: 10.1007/s00774-016-0806-3. Epub 2016 Dec 20. | ||||
| 8 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 9 | FDA Approved Drug Products: Zometa Zoledronic Acid Intravenous Injection | ||||
| 10 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 11 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 12 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 13 | Zoledronic acid is synergic with vinblastine to induce apoptosis in a multidrug resistance protein-1 dependent way: an in vitro study. Cell Biol Int. 2006 Mar;30(3):278-82. | ||||
| 14 | Interleukin-19 as a translational indicator of renal injury. Arch Toxicol. 2015 Jan;89(1):101-6. | ||||
| 15 | The proapoptotic effect of zoledronic acid is independent of either the bone microenvironment or the intrinsic resistance to bortezomib of myeloma cells and is enhanced by the combination with arsenic trioxide. Exp Hematol. 2011 Jan;39(1):55-65. | ||||
| 16 | Zoledronate dysregulates fatty acid metabolism in renal tubular epithelial cells to induce nephrotoxicity. Arch Toxicol. 2018 Jan;92(1):469-485. | ||||
| 17 | Banerjee D, Asif A, Striker L, Preston RA, Bourgoignie JJ, Roth D "Short-term, high-dose pamidronate-induced acute tubular necrosis: The postulated mechanisms of bisphosphonate nephrotoxicity." Am J Kidney Dis 41 (2003): E18. [PMID: 12778436] | ||||
| 18 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 19 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 20 | Wong GT, Lee EY, Irwin MG. Contrast induced nephropathy in vascular surgery.?Br J Anaesth. 2016;117 Suppl 2:ii63-ii73. [PMID: 27566809] | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Eloxatin (oxaliplatin). Sanofi Winthrop Pharmaceuticals, New York, NY. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Skelid (tilundronate). Sanofi Winthrop Pharmaceuticals, New York, NY. | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Zometa (zoledronic acid). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Actonel (risedronate). Procter and Gamble Pharmaceuticals, Cincinnati, OH. | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Clolar (clofarabine). sanofi-aventis, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Exjade (deferasirox). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Prograf (tacrolimus). Fujisawa, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
