Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMPIHLS)
| Drug Name |
Diclofenac
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms | Diclofenac (sodium matrix patch, pain) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Neurology Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
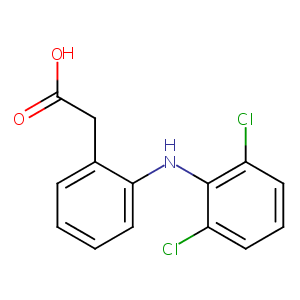 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 296.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 4.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Diclofenac
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Diclofenac (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Diclofenac FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | ||||
| 3 | Davies NM, Anderson KE: Clinical pharmacokinetics of diclofenac. Therapeutic insights and pitfalls. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997 Sep;33(3):184-213. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199733030-00003. | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS predictions, self-correcting aspects of BDDCS assignments, BDDCS assignment corrections, and classification for more than 175 additional drugs | ||||
| 5 | Todd PA, Sorkin EM: Diclofenac sodium. A reappraisal of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs. 1988 Mar;35(3):244-85. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198835030-00004. | ||||
| 6 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 7 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 8 | Diclofenac and NS-398, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, decrease agonist-induced contractions of the pig isolated ureter. Urol Res. 2000 Dec;28(6):376-82. | ||||
| 9 | Transport of diclofenac by breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) and stimulation of multidrug resistance protein 2 (ABCC2)-mediated drug transport by diclofenac and benzbromarone. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009 Jan;37(1):129-36. | ||||
| 10 | Influence of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) 1B1- and OATP1B3-mediated drug transport. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011 Jun;39(6):1047-53. | ||||
| 11 | Cytochrome P450 3A4-mediated interaction of diclofenac and quinidine. Drug Metab Dispos. 2000 Sep;28(9):1043-50. | ||||
| 12 | New insights into the structural features and functional relevance of human cytochrome P450 2C9. Part I. Curr Drug Metab. 2009 Dec;10(10):1075-126. | ||||
| 13 | Diclofenac and its derivatives as tools for studying human cytochromes P450 active sites: particular efficiency and regioselectivity of P450 2Cs. Biochemistry. 1999 Oct 26;38(43):14264-70. | ||||
| 14 | Metabolism and metabolic inhibition of xanthotoxol in human liver microsomes. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:5416509. | ||||
| 15 | Hepatic metabolism of diclofenac: role of human CYP in the minor oxidative pathways. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999 Sep 1;58(5):787-96. | ||||
| 16 | Analysis of human cytochrome P450 2C8 substrate specificity using a substrate pharmacophore and site-directed mutants. Biochemistry. 2004 Dec 14;43(49):15379-92. | ||||
| 17 | Substrates, inducers, inhibitors and structure-activity relationships of human Cytochrome P450 2C9 and implications in drug development. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(27):3480-675. | ||||
| 18 | Glucuronidation of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: identifying the enzymes responsible in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2005 Jul;33(7):1027-35. | ||||
| 19 | Broad substrate specificity of human cytochrome P450 46A1 which initiates cholesterol degradation in the brain. Biochemistry. 2003 Dec 9;42(48):14284-92. | ||||
| 20 | Both reactivity and accessibility are important in cytochrome P450 metabolism: a combined DFT and MD study of fenamic acids in BM3 mutants. J Chem Inf Model. 2019 Feb 25;59(2):743-753. | ||||
| 21 | The metagenome of Caracolus marginella gut microbiome using culture independent approaches and shotgun sequencing. Data Brief. 2017 Nov 22;16:501-505. | ||||
| 22 | Hydroxylation of Compactin (ML-236B) by CYP105D7 (SAV_7469) from Streptomyces avermitilis. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 May 28;27(5):956-964. | ||||
| 23 | Drug-induced endoplasmic reticulum and oxidative stress responses independently sensitize toward TNF-mediated hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Sci. 2014 Jul;140(1):144-59. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu072. Epub 2014 Apr 20. | ||||
| 24 | Gene expression profiling of rheumatoid arthritis synovial cells treated with antirheumatic drugs. J Biomol Screen. 2007 Apr;12(3):328-40. doi: 10.1177/1087057107299261. Epub 2007 Mar 22. | ||||
| 25 | 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) is up-regulated by flurbiprofen and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in human colon cancer HT29 cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2009 Jul 15;487(2):139-45. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2009.05.017. Epub 2009 Jun 6. | ||||
| 26 | Antirheumatic drug response signatures in human chondrocytes: potential molecular targets to stimulate cartilage regeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(1):R15. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Solaraze (diclofenac topical). Doak Dermatologics Division, Fairfield, NJ. | ||||
| 28 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 29 | Abad S, Moachon L, Blanche P, Bavoux F, Sicard D, Salmon-Ceron D "Possible interaction between glicazide, fluconazole and sulfamethoxazole resulting in severe hypoglycaemia." Br J Clin Pharmacol 52 (2001): 456-7. [PMID: 11678792] | ||||
| 30 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 31 | Altman R, Scazziota A, Dujovne C "Diltiazem potentiates the inhibitory effect of aspirin on platelet aggregation." Clin Pharmacol Ther 44 (1988): 320-5. [PMID: 3416553] | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Acular (ketorolac). Allergan Inc, Irvine, CA. | ||||
| 34 | Buchman AL, Schwartz MR "Colonic ulceration associated with the systemic use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medication." J Clin Gastroenterol 22 (1996): 224-6. [PMID: 8724264] | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Factive (gemifloxacin). GeneSoft Inc, San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 36 | Assael BM, Chiabrando C, Gagliardi L, Noseda A, Bamonte F, Salmona M "Prostaglandins and aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity." Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 78 (1985): 386-94. [PMID: 4049389] | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Actonel (risedronate). Procter and Gamble Pharmaceuticals, Cincinnati, OH. | ||||
| 38 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Tykerb (lapatinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Piqray (alpelisib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 41 | Wong GT, Lee EY, Irwin MG. Contrast induced nephropathy in vascular surgery.?Br J Anaesth. 2016;117 Suppl 2:ii63-ii73. [PMID: 27566809] | ||||
| 42 | Alderman CP, Moritz CK, Ben-Tovim DI "Abnormal platelet aggregation associated with fluoxetine therapy." Ann Pharmacother 26 (1992): 1517-9. [PMID: 1482806] | ||||
| 43 | Bang CJ, Riedel B, Talstad I, Berstad A "Interaction between heparin and acetylsalicylic acid on gastric mucosal and skin bleeding in humans." Scand J Gastroenterol 27 (1992): 489-94. [PMID: 1321488] | ||||
| 44 | Product Information. Korlym (mifepristone). Corcept Therapeutics Incorporated, Menlo Park, CA. | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Kalydeco (ivacaftor). Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 46 | Product Information. Prevymis (letermovir). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Xarelto (rivaroxaban). Bayer Inc, Toronto, IA. | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Emend (aprepitant). Merck & Company Inc, West Point, PA. | ||||
| 49 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 50 | EMEA. European Medicines Agency "EPARs. European Union Public Assessment Reports.". | ||||
| 51 | Muller FO, Schall R, Devaal AC, Groenewoud G, Hundt HKL, Middle MV "Influence of meloxicam on furosemide pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healthy volunteers." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 48 (1995): 247-51. [PMID: 7589049] | ||||
| 52 | Abdel-Haq B, Magagna A, Favilla S, Salvetti A "Hemodynamic and humoral interactions between perindopril and indomethacin in essential hypertensive subjects." J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 18 (1991): s33-6. [PMID: 1725198] | ||||
| 53 | Product Information. Priftin (rifapentine). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 54 | Product Information. Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 55 | Elsharkawy AM, Schwab U, McCarron B, et al. "Efavirenz induced acute liver failure requiring liver transplantation in a slow drug metaboliser." J Clin Virol 58 (2013): 331-3. [PMID: 23763943] | ||||
| 56 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 57 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 58 | EMEA "EMEA public statement on leflunomide (ARAVA) - severe and serious hepatic reactions.". | ||||
| 59 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 60 | Product Information. Potassium Chloride ER (potassium chloride). Zydus Pharmaceuticals (USA) Inc, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 61 | Novis BH, Korzets Z, Chen P, Bernheim J "Nephrotic syndrome after treatment with 5-aminosalicylic acid." Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 296 (1988): 1442. [PMID: 3132281] | ||||
| 62 | Blakely KM, Drucker AM, Rosen CF "Drug-induced photosensitivity-an update: Culprit drugs, prevention and management." Drug Saf 42 (2019): 827-47. [PMID: 30888626] | ||||
| 63 | Caruso V, Iacoviello L, Di Castelnuovo A, et.al "Thrombotic complications in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a meta-analysis of 17 prospective studies comprising 1752 pediatric patients." Blood 108 (2006): 2216-22. [PMID: 16804111] | ||||
| 64 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 65 | Product Information. Calquence (acalabrutinib). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 66 | Agencia Espaola de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios Healthcare "Centro de informacion online de medicamentos de la AEMPS - CIMA.". | ||||
| 67 | Product Information. Iclusig (ponatinib). Ariad Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 68 | Product Information. Exjade (deferasirox). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 69 | Product Information. Tasigna (nilotinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 70 | Product Information. Gleevec (imatinib mesylate). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 71 | Product Information. Sprycel (dasatinib). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 72 | Product Information. Brukinsa (zanubrutinib). BeiGene USA, Inc, San Mateo, CA. | ||||
| 73 | Product Information. Zontivity (vorapaxar). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 74 | Product Information. Integrilin (eptifibatide). Schering Laboratories, Kenilworth, NJ. | ||||
| 75 | Doherty MM, Charman WN "The mucosa of the small intestine: how clinically relevant as an organ of drug metabolism?" Clin Pharmacokinet 41 (2002): 235-53. [PMID: 11978143] | ||||
| 76 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 77 | Product Information. Fycompa (perampanel). Eisai Inc, Teaneck, NJ. | ||||
| 78 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 79 | Product Information. Flolan (epoprostenol). Glaxo Wellcome, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 80 | Product Information. Prograf (tacrolimus). Fujisawa, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 81 | Product Information. ReVia (naltrexone). DuPont Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 82 | Product Information. Ferriprox (deferiprone). ApoPharma USA Inc, Rockville, MD. | ||||
| 83 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 84 | Product Information. Cometriq (cabozantinib). Exelixis Inc, S San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 85 | Product Information. Bevyxxa (betrixaban). Portola Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
