Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMMX2E6)
| Drug Name |
Pemetrexed
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Alimta; LYA; LY 231514; LY231514; Alimta (TN); LY 231,514; LY-2315; LY-231514; Pemetrexed (INN); Pemetrexed [INN:BAN]; LY-231,514; N-(4-(2-(2-Amino-3,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7H-pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimdin-5-yl)ethyl)benzoyl)glutamic acid; N-{4-[2-(2-amino-4-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-5-yl)ethyl]benzoyl}-d-glutamic acid; (2R)-2-[[4-[2-(2-amino-4-oxo-1,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-5-yl)ethyl]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid; (2S)-2-[[4-[2-(2-amino-4-oxo-1,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-5-yl)ethyl]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid; 2-[[4-[2-(2-amino-4-oxo-1,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-5-yl)ethyl]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid; 2-{4-[2-(2-AMINO-4-OXO-4,7-DIHYDRO-3H-PYRROLO[2,3-D]PYRIMIDIN-5-YL)-ETHYL]-BENZOYLAMINO}-PENTANEDIOIC ACID
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anticancer Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
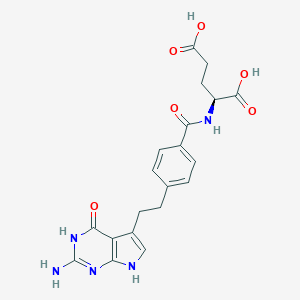 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 1 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 427.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Experimental Cancer Drug Sensitivity Information
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Pemetrexed (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
| 1 | Pemetrexed FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6837). | ||||
| 3 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 4 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 5 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 6 | Updated clinical information on multitargeted antifolates in lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009 Mar;10 Suppl 1:S35-40. | ||||
| 7 | Biology of the major facilitative folate transporters SLC19A1 and SLC46A1. Curr Top Membr. 2014;73:175-204. | ||||
| 8 | The proton-coupled folate transporter: impact on pemetrexed transport and on antifolates activities compared with the reduced folate carrier. Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Sep;74(3):854-62. | ||||
| 9 | Kinetic validation of the use of carboxydichlorofluorescein as a drug surrogate for MRP5-mediated transport. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006 Apr;27(5):524-32. | ||||
| 10 | Human intestinal transporter database: QSAR modeling and virtual profiling of drug uptake, efflux and interactions. Pharm Res. 2013 Apr;30(4):996-1007. | ||||
| 11 | Substrate- and pH-specific antifolate transport mediated by organic anion-transporting polypeptide 2B1 (OATP2B1-SLCO2B1). Mol Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;81(2):134-42. | ||||
| 12 | pH-Dependent transport of pemetrexed by breast cancer resistance protein. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011 Sep;39(9):1478-85. | ||||
| 13 | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene rearrangements in non-small cell lung cancer are associated with prolonged progression-free survival on pemetrexed. J Thorac Oncol. 2011 Apr;6(4):774-80. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31820cf053. | ||||
| 14 | ABCC11/MRP8 confers pemetrexed resistance in lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010 Nov;101(11):2404-10. | ||||
| 15 | The multidrug resistance protein 5 (ABCC5) confers resistance to 5-fluorouracil and transports its monophosphorylated metabolites. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005 May;4(5):855-63. | ||||
| 16 | Xanthohumol inhibits non-small cell lung cancer by activating PUMA-mediated apoptosis. Toxicology. 2022 Mar 30;470:153141. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2022.153141. Epub 2022 Mar 5. | ||||
| 17 | KRAS mutation status is associated with enhanced dependency on folate metabolism pathways in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Jun;13(6):1611-24. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0649. Epub 2014 Mar 31. | ||||
| 18 | Death receptor 5 and cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein regulate pemetrexed-induced apoptosis in human lung cancer cells. Eur J Cancer. 2011 Nov;47(16):2471-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.06.003. Epub 2011 Jul 2. | ||||
| 19 | Changes in the status of p53 affect drug sensitivity to thymidylate synthase (TS) inhibitors by altering TS levels. Br J Cancer. 2007 Mar 12;96(5):769-75. | ||||
| 20 | Pemetrexed downregulates ERCC1 expression and enhances cytotoxicity effected by resveratrol in human nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2013 Dec;386(12):1047-59. doi: 10.1007/s00210-013-0905-9. Epub 2013 Aug 3. | ||||
| 21 | A randomized, double-blind, phase II study of two doses of pemetrexed as first-line chemotherapy for advanced breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Jun 15;13(12):3652-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2377. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Alimta (pemetrexed). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 23 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Arava (leflunomide). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Prolia (denosumab). Amgen USA, Thousand Oaks, CA. | ||||
| 26 | Bennett CL, Nebeker JR, Samore MH, et al "The Research on Adverse Drug Events and Reports (RADAR) project." JAMA 293 (2005): 2131-40. [PMID: 15870417] | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Vumerity (diroximel fumarate). Alkermes, Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 28 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Gilenya (fingolimod). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Ocrevus (ocrelizumab). Genentech, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Synribo (omacetaxine). Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, North Wales, PA. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Arcalyst (rilonacept). Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc, Tarrytown, NY. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Cimzia (certolizumab). UCB Pharma Inc, Smyrna, GA. | ||||
| 34 | CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/ "Recommendations of the advisory committtee on immunization practices (ACIP): use of vaccines and immune globulins in persons with altered immunocompetence." MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 42(RR-04) (1993): 1-18. [PMID: 20300058] | ||||
