Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMOL5IU)
| Drug Name |
Mesalazine
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Apriso; Asacol; Asacolitin; Asacolon; Asalit; Ascolitin; Canasa; Claversal; Fisalamine; Fivasa; Iialda; Ipocol; Lialda; Lixacol; Mesacol; Mesalamine; Mesalazina; Mesalazinum; Mesasal; Mesavance; Mesavancol; Mezavant; Pentacol; Pentasa; Rowasa; Salofalk; Salozinal; SfRowasa; Allphar Brand of Mesalamine; Antigen Brand of Mesalamine; Asacol HD; Axcan Brand of Mesalamine; Byk Brand of Mesalamine; Celltech Brand of Mesalamine; Falk Brand of Mesalamine; Farmasa Brand of Mesalamine; Ferring Brand of Mesalamine; GlaxoSmithKline Brand of Mesalamine; Henning Berlin Brand of Mesalamine; M Aminosalicylic Acid; Merckle Brand of Mesalamine; Mesalamine Hydrochloride; Mesalamine Monosodium Salt; Mesalamine [USAN]; Mesalazina[Spanish]; Mesalazine MMX; Mesalazinum [Latin]; Meta Aminosalicylic Acid; Mezavant XL; Minosalicylic acid; Norgine Brand of Mesalamine; Novopharm Brand of Mesalamine; Provalis Brand of Mesalamine; Sanofi Synthelabo Brand of Mesalamine; Schering Plough Brand of Mesalamine; SmithKline Brand of Mesalamine; Solvay Brand of Mesalamine; Yamanouchi Brand of Mesalamine; Novo 5 ASA; Novo5 ASA; AJG-501; Apriso (TN); Asacol (TN); Canasa (TN); Hydrochloride, Mesalamine; Iialda (TN); Ipocal (TN); Lialda (TN); M-A; M-Aminosalicylic acid; MAX-002; MD-0901; Masacol (TN); Mesalamine (USP); Meta-AminosalicylicAcid; Monosodium Salt, Mesalamine; Novo-5 ASA; P-Aminosalicylsaeure; P-Aminosalicylsaeure [German]; Pentasa (TN); Procter & Gamble Brand of Mesalamine; Rowasa (TN); SPD-476; SPD-480; Salofalk (TN); Salofalk Granu-Stix; Schering-Plough Brand of Mesalamine; Z-206; Mesalazine (JAN/INN); Salicylic acid, 5-amino-(8CI); 2-Hydroxy-5-aminobenzoic acid; 3-carboxy-4-hydroxyaniline; 5 Aminosalicylate; 5 Aminosalicylic Acid; 5-AS; 5-ASA; 5-Amino-2-hydroxybenzoic acid; 5-Aminosalicylate; 5-Aminosalicylic acid; 5-amino-2-hydroxy-benzoic acid; 5-aminosalicylic acid, Mesalazine, Asacol, Pentasa, Canasa, Mesalamine
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinflammatory Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
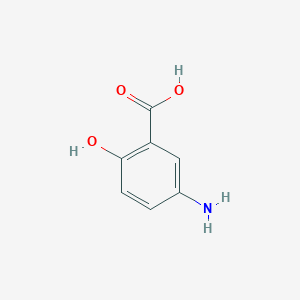 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 153.14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Diverticulitis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Mesalazine (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Colonic diverticular disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020 Mar 26;6(1):20. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Optimized Management of Ulcerative Proctitis: When and How to Use Mesalazine Suppository. Digestion. 2018;97(1):59-63. | ||||
| 3 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4655). | ||||
| 4 | Efficacy of Oral, Topical, or Combined Oral and Topical 5-Aminosalicylates, in Ulcerative Colitis: Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. J Crohns Colitis. 2021 Jul 5;15(7):1184-1196. | ||||
| 5 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 6 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 7 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 8 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | ||||
| 9 | Transport studies with 5-aminosalicylate. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2006 Oct;62(10):871-5. | ||||
| 10 | Role of organic anion-transporting polypeptides for cellular mesalazine (5-aminosalicylic acid) uptake. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011 Jun;39(6):1097-102. | ||||
| 11 | NAT1 genotypes do not predict response to mesalamine in patients with ulcerative colitis. Z Gastroenterol. 2008 Mar;46(3):259-65. | ||||
| 12 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 13 | Christensen LK, Hansen JM, Kristensen M "Sulphaphenazole-induced hypoglycemic attacks in tolbutamide-treated diabetics." Lancet 2 (1963): 1298-301. [PMID: 14071924] | ||||
| 14 | Lowry PW, Szumlanski CL, Weinshilboum RM, Sandborn WJ "Balsalazide and azathiprine or 6-mercaptopurine: evidence for a potentially serious drug interaction [letter comment." Gastroenterology 116 (1999): 1505-6. [PMID: 10391741] | ||||
| 15 | Product Information. Canasa (mesalamine (5-aminosalicylic acid)). Axcan Scandipharm Inc, Birmingham, AL. | ||||
| 16 | Chang JT, Green L, Beitz J "Renal failure with the use of zoledronic acid." N Engl J Med 349 (2003): 1676-9 discussion 1676-9. [PMID: 14573746] | ||||
| 17 | Bentley ML, Corwin HL, Dasta J "Drug-induced acute kidney injury in the critically ill adult: recognition and prevention strategies." Crit Care Med 38(6 Suppl) (2010): S169-74. [PMID: 20502171] | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Eloxatin (oxaliplatin). Sanofi Winthrop Pharmaceuticals, New York, NY. | ||||
| 19 | Product Information. Vistide (cidofovir). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 20 | Product Information. Clolar (clofarabine). sanofi-aventis, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Exjade (deferasirox). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Alimta (pemetrexed). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Prograf (tacrolimus). Fujisawa, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
